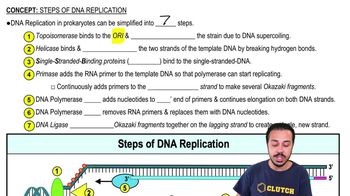
Steps of DNA Replication exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
Topoisomerase
An enzyme that relieves DNA supercoiling during DNA replication.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
Helicase unwinds the DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases.
Single-stranded binding proteins (SSBs)
Proteins that bind to single-stranded DNA to prevent reannealing and protect it from degradation.
What does primase do during DNA replication?
Primase adds RNA primers to the template DNA to provide a starting point for DNA polymerase.
DNA polymerase III
An enzyme that extends the DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the RNA primers.
What is the function of DNA polymerase I?
DNA polymerase I replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides.
DNA ligase
An enzyme that joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand to create a continuous DNA strand.
What is the first step of DNA replication in prokaryotes?
Topoisomerase relieves DNA supercoiling.
What happens in the second step of DNA replication?
Helicase unwinds the DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases.
What is the role of single-stranded binding proteins?
They prevent the single-stranded DNA from reannealing and protect it from degradation.
What is the fourth step of DNA replication?
Primase adds RNA primers to the template DNA.
What does DNA polymerase III do in the fifth step of DNA replication?
It extends the DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the RNA primers.
What occurs in the sixth step of DNA replication?
DNA polymerase I replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides.
What is the final step of DNA replication?
DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
Origin of replication
The specific sequence where DNA replication begins.
Replication fork
The area where the DNA double helix is unwound to allow replication of each strand.
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA fragments synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
What is the role of RNA primers in DNA replication?
They provide a starting point for DNA polymerase to begin DNA synthesis.
Leading strand
The DNA strand that is synthesized continuously in the direction of the replication fork.
Lagging strand
The DNA strand that is synthesized discontinuously in short fragments opposite to the direction of the replication fork.
What enzyme is responsible for adding nucleotides to the 3' end of the RNA primers?
DNA polymerase III.
What enzyme removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA?
DNA polymerase I.
What enzyme joins Okazaki fragments together?
DNA ligase.
What is the function of the replication fork?
It is the area where the DNA double helix is unwound to allow replication of each strand.
What are Okazaki fragments?
Short DNA fragments synthesized on the lagging strand during DNA replication.
What is the role of the leading strand in DNA replication?
It is synthesized continuously in the direction of the replication fork.
What is the role of the lagging strand in DNA replication?
It is synthesized discontinuously in short fragments opposite to the direction of the replication fork.
What is the role of topoisomerase in DNA replication?
It relieves DNA supercoiling.
What is the role of helicase in DNA replication?
It unwinds the DNA strands by breaking hydrogen bonds between them.