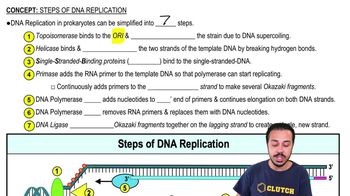
Steps of DNA Replication definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (7)
RNA Primers
Short RNA sequences that provide a starting point for DNA synthesis during replication, later replaced by DNA nucleotides.
DNA Replication
The process by which a cell duplicates its DNA, involving enzymes like DNA polymerase 1 to replace RNA primers with DNA, ensuring accurate genetic information is passed to daughter cells.
DNA Polymerase
An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to an existing primer during DNA replication and also replaces RNA primers with DNA nucleotides.
DNA Polymerase 1
An enzyme that removes RNA primers from the newly synthesized DNA strand and replaces them with DNA nucleotides during DNA replication.
DNA Polymerase 3
The enzyme responsible for synthesizing new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to an RNA primer during DNA replication.
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotide pairs, allowing replication or transcription to occur.
Primase
An enzyme that synthesizes short RNA sequences called primers, which serve as starting points for DNA synthesis during replication.