Species quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackSpecies quiz
1/19
Terms in this set (19)
- What is the morphological species concept?The morphological species concept defines species based on morphological features, such as outward appearance and internal physiological similarities.
- How does the ecological species concept define species?The ecological species concept defines species in terms of their niche, which is their specific role in their environment.
- Why doesn't the biological species concept work well for asexual species?The biological species concept relies on sexual reproduction, which is not applicable to asexual species.
- What is the phylogenetic species concept?The phylogenetic species concept defines species based on the smallest group of individuals sharing a common ancestor on the phylogenetic tree.
- What is allopatric speciation?Allopatric speciation is speciation that begins with geographic isolation, leading to the divergence of species over a long period.
- How does sympatric speciation differ from allopatric speciation?Sympatric speciation occurs in populations that live in the same geographic area, often due to disruptive selection or polyploidy.
- What is polyploidy and how does it contribute to speciation?Polyploidy is the doubling of chromosome number due to meiotic or mitotic errors, which can lead to speciation, especially in plants.
- What is reinforcement in the context of speciation?Reinforcement is natural selection for traits that isolate a population, reinforcing barriers between species.
- What is a hybrid zone?A hybrid zone is a geographic region where interspecies breeding occurs and hybrids are common.
- What are the three possible outcomes in a hybrid zone?The three possible outcomes are reinforcement, fusion, and stability.
- What is continental drift?Continental drift is the movement of tectonic plates, resulting in the shifting of continents over time.
- What was Pangaea?Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed on Earth, made up of all the Earth's land masses combined.
- What are Laurasia and Gondwana?Laurasia and Gondwana were two giant land masses that formed after the breakup of Pangaea.
- How does plate tectonics relate to the distribution of species?Plate tectonics causes continental drift, which can lead to geographic isolation and speciation.
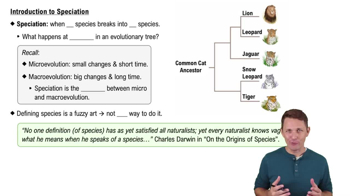
- What is the significance of the phylogenetic tree in defining species?The phylogenetic tree helps define species by showing the smallest group of individuals sharing a common ancestor.
- _____ is rapid speciation under conditions in which there is little competition.Adaptive radiation is rapid speciation under conditions in which there is little competition.
- which of these statements defines speciation?Speciation is the process where an ancestral species diverges into two or more species, often due to reproductive isolation.
- what process can promote speciation through random changes between isolated populations?Genetic drift can promote speciation through random changes between isolated populations.
- what prevents speciation from occurring in sympatric populations?Gene flow prevents speciation from occurring in sympatric populations by maintaining genetic similarity.