Signal Amplification exam Flashcards
 Back
BackSignal Amplification exam
1/28
Terms in this set (28)
- Signal AmplificationOccurs when a signaling molecule binds to its receptor, leading to a larger cellular response through the activation of multiple molecules.
- What is the role of protein kinases in signal amplification?Protein kinases add phosphate groups to proteins, which can activate or deactivate them, playing a crucial role in signal amplification.
- PhosphorylationThe process of adding a phosphate group to a protein, altering its activity.
- What happens when a signaling molecule binds to its receptor?It can cause a conformational change in the receptor, leading to signal amplification or a smaller cellular response.
- Protein PhosphatasesEnzymes that remove phosphate groups from proteins, often deactivating them.
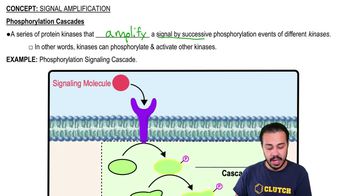
- What is a phosphorylation cascade?A series of protein kinases that amplify a signal by successive phosphorylation events of different kinases.
- Conformational ChangeA structural change in a receptor that occurs when a signaling molecule binds to it.
- How do protein kinases and protein phosphatases differ?Protein kinases add phosphate groups to proteins, while protein phosphatases remove them.
- Cellular ResponseThe outcome or effect within a cell following signal amplification.
- What is the source of the phosphate group in phosphorylation?ATP, which gets hydrolyzed into ADP.
- Dephosphorylated ProteinA protein that does not have a phosphate group attached.
- What is the effect of phosphorylation on a protein?It alters the protein's activity, either activating or deactivating it.
- Phosphorylated ProteinA protein that has a phosphate group attached, often leading to altered activity.
- What is the role of ATP in phosphorylation?ATP provides the phosphate group that is added to proteins during phosphorylation.
- Signal MoleculeA molecule that binds to a receptor to initiate signal amplification.
- What happens in a phosphorylation signaling cascade?A kinase enzyme becomes phosphorylated and activates other kinases in a series of successive phosphorylation events.
- Extracellular FluidThe fluid outside of a cell where signaling molecules are often found.
- What is the function of protein phosphatases in signal amplification?They remove phosphate groups from proteins, often deactivating them and dampening the cellular response.
- CytoplasmThe inside of the cell where signal amplification processes occur.
- What is the result of signal amplification?A larger cellular response due to the activation of many molecules.
- ReceptorA protein embedded in the cell membrane that binds to signaling molecules.
- How does signal amplification maximize cellular response?By activating many molecules, leading to a larger and more effective cellular response.
- Phosphorylation EventsSuccessive actions where kinases add phosphate groups to proteins, amplifying the signal.
- What is the importance of understanding signal amplification?It is crucial for grasping cellular communication and response dynamics in biological systems.
- Kinase EnzymeAn enzyme that adds phosphate groups to proteins, playing a key role in phosphorylation cascades.
- What does a conformational change in a receptor lead to?It can lead to either signal amplification or a smaller cellular response.
- Phosphate GroupA chemical group added to proteins by kinases, altering their activity.
- What is the role of phosphorylation in signal amplification?Phosphorylation alters protein activity, which can activate other proteins and amplify the signal.