Sensory System definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (10)
Sensory System
The part of the nervous system that detects, transduces, and processes sensory stimuli, enabling perception and interaction with the environment through specialized receptors for different types of stimuli.
Receptor Potential
A graded electrical response in a sensory receptor cell, caused by the activation of the receptor by a stimulus, which can lead to the generation of action potentials if the threshold is reached.
Sensory Adaptation
The process where sensory receptors become less responsive to a constant stimulus over time, allowing the nervous system to focus on changes in the environment.
Mechanoreceptors
Nerve cells that detect physical stimuli like pressure, vibration, and stretch, converting them into electrical signals for the brain to interpret.
Proprioceptors
Sensory receptors in muscles and joints that detect body position and movement, aiding in balance and posture maintenance.
Nociceptors
Specialized nerve cells that detect tissue damage or potential harm, leading to the perception of pain. They respond to mechanical, thermal, and chemical stimuli, signaling the brain to initiate protective responses.
Chemoreceptors
Sensory receptors that detect chemical stimuli, such as those in the nose for smell or on the tongue for taste, converting chemical signals into nerve impulses.
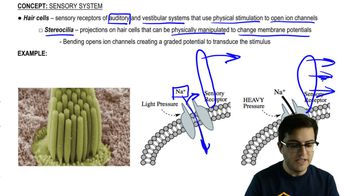
Hair Cells
Sensory receptors in the auditory and vestibular systems, featuring hair-like projections called stereocilia, which bend to open ion channels, converting physical stimuli into neural signals.
Cochlea
A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure in the inner ear that converts sound vibrations into neural signals, enabling the perception of sound.
Rhodopsin
A light-sensitive receptor protein in rod cells of the retina, crucial for low-light vision, composed of opsin and retinal, which changes shape upon absorbing light, triggering a neural response.