Seed Plants exam Flashcards
 Back
BackSeed Plants exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- SporophyteThe dominant life cycle stage in seed plants, producing spores.
- What are the two main groups of seed plants?Angiosperms and gymnosperms.
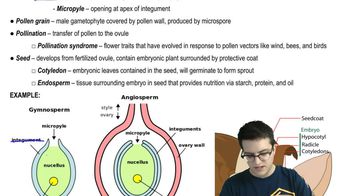
- HeterosporousProducing two types of spores: microspores and megaspores.
- What is the function of the integument in seed plants?It is the outer protective layer of the ovule.
- AngiospermsSeed plants that produce seeds within fruits.
- What is double fertilization?A process in angiosperms where one sperm fertilizes the egg and another forms the endosperm.
- GymnospermsSeed plants that produce naked seeds in cones.
- What are cotyledons?Embryonic leaves contained in the seed.
- MonocotsAngiosperms with one cotyledon.
- What is the role of the endosperm?It provides nutrition for the developing embryo.
- EudicotsAngiosperms with two cotyledons.
- What is pollination syndrome?Flower traits evolved in response to pollen vectors like wind, bees, and birds.
- Complete FlowerA flower that contains sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
- What is a micropyle?The opening at the apex of the integument in an ovule.
- Perfect FlowerA flower that has both male and female structures.
- What is the difference between monoecious and dioecious plants?Monoecious plants have both male and female flowers on the same plant, while dioecious plants have them on separate plants.
- StamenThe male part of the flower, consisting of the filament and anther.
- What is the function of the carpel in a flower?It is the female part of the flower, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
- Cross-PollinationTransfer of pollen from one plant to a different plant of the same species.
- What is self-pollination?When a plant fertilizes itself using its own pollen.
- PollinationThe transfer of pollen to the ovule.
- What are conifers?A group of gymnosperms known for their needle-like leaves and cones.
- OvuleThe structure that contains the megasporangium and develops into a seed after fertilization.
- What is the role of the pollen tube?It digests its way through the ovule to deliver sperm to the egg.
- IntegumentThe outer protective layer of the ovule.
- What is the function of the sepal?It encases and protects the flower bud before it opens.
- EmbryoThe developing plant within a seed.
- What is the significance of the ovary in angiosperms?It encloses the ovules and develops into fruit.
- Pollen GrainThe male gametophyte covered by a tough pollen wall.