Roots and Shoots definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (10)
Roots
Underground plant structures that absorb water and nutrients, anchor the plant, and store energy-rich compounds like sugars.
Shoots
Above-ground plant structures responsible for photosynthesis, gas exchange, and reproduction, including stems, leaves, and flowers.
Chloroplast
Organelle in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs, converting sunlight into chemical energy using chlorophyll, the green pigment that absorbs light.
Central Vacuole
A large, membrane-bound organelle in plant cells that stores water, nutrients, and waste, and helps maintain cell rigidity by exerting turgor pressure against the cell wall.
Plasmodesmata
Channels between plant cells that allow for the transport of materials and cell signaling.
Tap Root
A primary root that grows vertically downward, becoming the central, dominant root from which smaller lateral roots branch out.
Lateral Roots
Roots that branch off from the main root, increasing surface area for water and nutrient absorption, and aiding in plant stability.
Adventitious
Roots that develop from non-root tissues, such as stems or leaves, often aiding in support, propagation, or nutrient absorption.
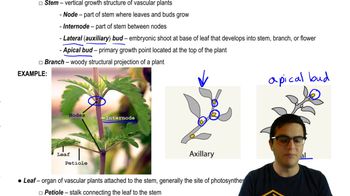
Nodes
Points on a plant stem where leaves, branches, or buds originate, crucial for plant growth and development.
Internode
The segment of a plant stem between two nodes, where no leaves or buds grow, allowing for elongation and spacing of leaves and branches.