r/K Selection exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
r/K Selection
Two contrasting life history strategies shaped by natural selection.
K-selected species
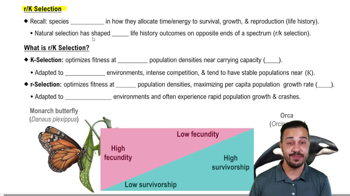
Species that thrive in stable environments near carrying capacity (K), with low fecundity and high parental investment.
r-selected species
Species that flourish in unstable conditions, maximizing growth rates (r) with high fecundity and minimal parental care.
What type of survivorship curve do K-selected species exhibit?
Type 1 survivorship curve.
What type of survivorship curve do r-selected species exhibit?
Type 3 survivorship curve.
Carrying capacity (K)
The maximum population size that an environment can sustain.
Fecundity
The reproductive capacity of an organism or population.
Parental investment
The time and energy parents expend for their offspring's benefit.
What is the main characteristic of r-selected species' environments?
Unstable environments.
What is the main characteristic of K-selected species' environments?
Stable environments.
Boom and bust cycles
Rapid population growth followed by rapid population crashes, typical of r-selected species.
Type 1 survivorship curve
Characterized by low mortality rates and high survivorship early in life, with increased mortality later in life.
Type 3 survivorship curve
Characterized by high mortality rates and low survivorship early in life, with lower mortality and higher survivorship in adulthood.
What is the reproductive strategy of K-selected species?
Producing few offspring with high parental investment.
What is the reproductive strategy of r-selected species?
Producing many offspring with low parental investment.
What does 'r' in r-selection stand for?
Per capita population growth rate.
What does 'K' in K-selection stand for?
Carrying capacity.
What type of species is represented by the monarch butterfly in r/K selection?
r-selected species.
What type of species is represented by the orca in r/K selection?
K-selected species.
What is the main focus of K-selection?
Optimizing fitness at high population densities near carrying capacity.
What is the main focus of r-selection?
Maximizing the per capita population growth rate.
Survivorship
The proportion of individuals surviving at each age interval.
What is a key difference between r-selected and K-selected species?
r-selected species have high fecundity and low parental care, while K-selected species have low fecundity and high parental care.
What kind of environments do K-selected species adapt to?
Stable environments with intense competition.
What kind of environments do r-selected species adapt to?
Unstable environments with less competition.
What is the trade-off in r/K selection?
Between fecundity and survivorship.
What happens to mortality rates in Type 1 survivorship curves later in life?
Mortality rates increase.