Review of Aerobic Cellular Respiration definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (7)
ATP
A molecule that stores and transfers energy within cells, produced mainly during aerobic cellular respiration, with a maximum yield of 38 per glucose molecule.
Glucose
A simple sugar that, when fully oxidized in aerobic respiration, yields 30-38 ATP molecules, serving as a primary energy source for cells.
Oxidation
The loss of electrons from a molecule, often accompanied by a gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen, resulting in energy release.
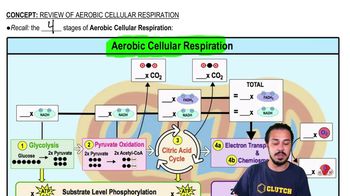
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP, producing 30-38 ATP molecules, primarily through the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes in mitochondria that transfer electrons, creating a proton gradient to produce ATP during aerobic respiration.
Chemiosmosis
The process where ATP is produced as protons move down their gradient through ATP synthase, following the electron transport chain in cellular respiration.
Efficiency
The ratio of useful energy output (ATP) to the total energy input (glucose) in aerobic cellular respiration, with a maximum yield of 38 ATP per glucose molecule.