Redox Reactions definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (8)
Glucose
A simple sugar and primary energy source for cells, undergoing oxidation to donate electrons to NAD+, forming NADH in metabolic processes.
NAD+
An oxidized electron carrier that accepts electrons during cellular respiration, converting to NADH.
NADH
A reduced form of an electron carrier that stores energy by accepting electrons during glucose oxidation.
Electron Carrier
A molecule that transports electrons during cellular respiration, facilitating energy production by alternating between oxidized and reduced states.
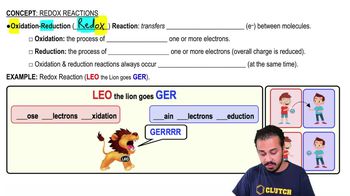
Oxidation
The process where a molecule loses electrons, often increasing its oxidation state, typically involving the transfer of electrons to an electron acceptor.
Reduction
The gain of electrons by a molecule, atom, or ion, often accompanied by a decrease in oxidation state.
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particles involved in chemical reactions, energy transfer, and redox processes, crucial for cellular respiration and metabolism.
FADH2
A molecule that acts as an electron carrier, accepting electrons during cellular respiration to form FADH2, which then donates electrons to the electron transport chain for ATP production.