Punnett Square Probability quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackPunnett Square Probability quiz
1/30
Terms in this set (30)
- What is the rule of multiplication also known as?The rule of multiplication is also known as the product rule or the and rule.
- How do you calculate the probability of two independent events both occurring?You multiply the probability of each event occurring independently.
- What is the probability of two coins both landing on tails?The probability is 1/4, calculated as 1/2 times 1/2.
- What does the rule of addition, also known as the sum rule or the or rule, involve?It involves adding the probabilities of one independent event or another independent event occurring.
- How do you calculate the probability of two coins both landing on heads or both landing on tails?You add the probabilities of each event: 1/4 (heads) + 1/4 (tails) = 1/2.
- What is the probability of having a homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive offspring?The probability is 1/2, calculated as 1/4 (dominant) + 1/4 (recessive).
- What is incomplete dominance?Incomplete dominance is a pattern of inheritance where heterozygous individuals show a blended phenotype that is intermediate between the two alleles.
- What phenotype results from a cross between a red flower (homozygous) and a white flower (homozygous) in incomplete dominance?The resulting phenotype is pink flowers.
- What is the probability that two heterozygous pea plants will both produce green offspring?The probability is 1/16, calculated as 1/4 (first offspring) times 1/4 (second offspring).
- What does the term 'allele' refer to in genetics?An allele is a variant form of a gene.
- How does the rule of multiplication apply to Punnett squares?It is used to calculate the probability of multiple independent genetic events occurring together.
- What is the probability of flipping a coin and it landing on heads?The probability is 1/2 or 50%.
- What is the probability of flipping two coins and both landing on heads?The probability is 1/4, calculated as 1/2 times 1/2.
- What is the probability of flipping two coins and both landing on tails?The probability is 1/4, calculated as 1/2 times 1/2.
- What is the probability of flipping two coins and either both landing on heads or both landing on tails?The probability is 1/2, calculated as 1/4 (heads) + 1/4 (tails).
- What is the probability of a coin landing on heads in a single flip?The probability is 50%, or 1/2.
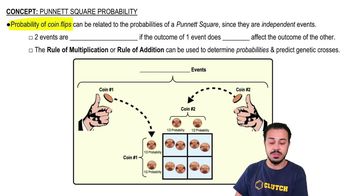
- How are coin flips related to Punnett square probabilities?Both represent independent events where the outcome of one event does not affect the outcome of another.
- What is the rule of multiplication in the context of Punnett squares?The rule of multiplication, or the 'and' rule, is used to determine the probability of multiple independent events occurring together.
- What is the probability of two heterozygous parents having a homozygous recessive offspring?The probability is 1/4 or 25%.
- How do you calculate the probability of having three homozygous recessive offspring from two heterozygous parents?Using the multiplication rule: 1/4 * 1/4 * 1/4 = 1/64.
- What is the rule of addition in the context of Punnett squares?The rule of addition, or the 'or' rule, is used to determine the probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring.
- What is the probability that a child will have the same genotype as a homozygous dominant father or a heterozygous mother?The probability is 100% because 1/2 (father's genotype) + 1/2 (mother's genotype) = 1.
- What does it mean for events to be independent in genetics?It means the outcome of one event does not affect the outcome of another event, similar to coin flips.
- What is the probability of a coin landing on tails in a single flip?The probability is 50%, or 1/2.
- How can you use coins to represent alleles in a Punnett square?Each coin flip represents an allele, and the combinations of heads and tails represent different genetic outcomes.
- What is the probability of having one homozygous dominant and one heterozygous offspring from a homozygous dominant and heterozygous cross?The probability is 1/2 for each genotype.
- What is the probability of two heterozygous parents having a homozygous dominant offspring?The probability is 1/4 or 25%.
- What is the probability of two heterozygous parents having a heterozygous offspring?The probability is 1/2 or 50%.
- What is the probability of a child having a genotype different from both parents if one parent is homozygous dominant and the other is heterozygous?The probability is 0% because the child will always have a genotype matching one of the parents.
- What is the probability of two heterozygous parents having at least one homozygous recessive offspring in three births?The probability is 1 - (3/4 * 3/4 * 3/4) = 37.5%.