Punnett Square Probability definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackPunnett Square Probability definitions
1/14
Terms in this set (14)
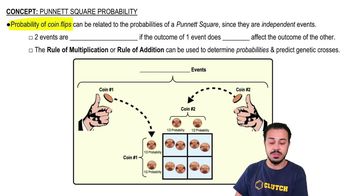
- Punnett SquareA grid used to predict the genotypes of offspring from a genetic cross, representing the combination of parental alleles as independent events.
- ProbabilityThe likelihood of a specific outcome occurring in a random event, often expressed as a fraction or percentage, and used to predict genetic trait distribution in Punnett squares.
- FertilizationThe union of male and female gametes, resulting in the formation of a zygote, each event being independent of others.
- Rule Of MultiplicationThe probability of two independent genetic events both occurring is the product of their individual probabilities.
- Rule Of AdditionThe probability of either of two mutually exclusive events occurring is the sum of their individual probabilities.
- Genetic CrossesThe process of predicting offspring genotypes by combining parental alleles using a Punnett square, considering independent events and probability rules.
- AllelesVariants of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome, influencing specific traits.
- Homozygous DominantHaving two identical dominant alleles for a specific gene, resulting in the expression of the dominant trait.
- HeterozygousHaving two different alleles for a specific gene, one inherited from each parent.
- Homozygous RecessiveHaving two identical recessive alleles for a trait, resulting in the expression of the recessive phenotype.
- GenotypeThe genetic makeup of an organism, consisting of the specific alleles inherited from its parents, determining its potential traits.
- OffspringThe result of reproduction, inheriting genetic material from parent organisms, often studied using Punnett squares to predict genetic traits.
- Coin FlipA random event with two equally likely outcomes, often used to illustrate independent probabilities in genetic crosses, such as predicting allele combinations in Punnett squares.
- Multiplication RuleCalculate the probability of multiple independent genetic events by multiplying the probabilities of each individual event.