Protist Lineages exam Flashcards
 Back
BackProtist Lineages exam
1/26
Terms in this set (26)
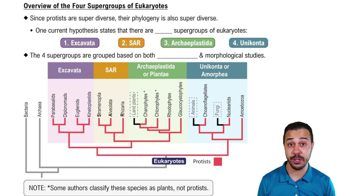
- ExcavataA major group of unicellular eukaryotes, many of which lack mitochondria and reproduce asexually.
- What is unique about Diplomonads?They lack mitochondria, have two nuclei, and use flagella for motion.
- ParabasalidsA group of protists that lack mitochondria and use flagella for movement, often parasitic.
- What is a mixotroph?An organism that can perform both photosynthesis and heterotrophy.
- ArchaeplastidaA major monophyletic group of eukaryotes that includes green algae and land plants, originating from primary endosymbiosis.
- What pigment gives red algae its color?Phycoerythrin, which masks the green from chlorophyll.
- Green AlgaeA group of algae similar to land plants, containing chlorophytes and charophytes.
- What defines the SAR clade?A monophyletic supergroup made up of Stramenopiles, Alveolates, and Rhizarians.
- StramenopilesA group of protists characterized by flagella with hair-like projections, includes diatoms and brown algae.
- What are diatoms known for?Unicellular photosynthetic organisms with protective shells made of silicon dioxide.
- Golden AlgaeUnicellular organisms with yellow and brown carotenoids, often mixotrophs.
- What is the function of gas-filled chambers in brown algae?To help the kelp stalks float to the surface for better sunlight exposure.
- AlveolataA group of protists with membrane-enclosed sacs (alveoli) under the plasma membrane.
- What are dinoflagellates?Mostly unicellular aquatic protists with two flagella and cellulose plates.
- ApicomplexansParasitic protists with apical complex structures for host cell penetration.
- What is unique about the life cycle of Plasmodium?It involves both sexual and asexual reproduction, switching between mosquitoes and humans.
- CiliatesProtists covered in cilia used for movement and feeding, with a diploid micronucleus and macronucleus.
- How do ciliates reproduce sexually?By exchanging haploid micronuclei and undergoing mitosis to form new macronuclei and micronuclei.
- RhizariansMostly unicellular amoebas that use pseudopodia for feeding.
- What are radiolarians?Protists with an internal silica skeleton and pseudopodia for feeding.
- ForamsProtists with calcium carbonate shells that have holes for pseudopodia.
- What are Cercozoans?A group of amoeba and flagellated protists that feed with pseudopodia.
- AmoebozoaA group of amoebas with lobe and tube-shaped pseudopodia, including slime molds.
- What is a plasmodial slime mold?A large, continuous cell with many nuclei that forms fruiting bodies.
- Cellular Slime MoldsSlime molds that form fruiting bodies by aggregating individual cells.
- What is the significance of protists?They highlight the evolutionary diversity and complexity of eukaryotic life forms.