Protist Cells definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (15)
Chloroplasts
Organelles in plant and algal cells where photosynthesis occurs, originating from cyanobacteria through primary endosymbiosis, and sometimes having multiple membranes due to secondary endosymbiosis.
Primary Endosymbiosis
The process where a eukaryotic cell engulfs a cyanobacterium, which then evolves into a chloroplast, providing the cell with photosynthetic capabilities.
Cyanobacterium
A photosynthetic bacterium with a double membrane, engulfed by early eukaryotes, leading to the formation of chloroplasts in plants and some protists through primary and secondary endosymbiosis.
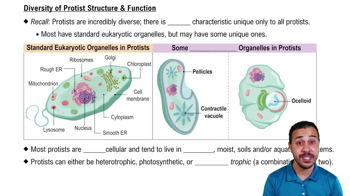
Protists
Eukaryotic organisms that don't fit into fungi, animalia, or plantae; often unicellular, sometimes multicellular, with diverse modes of nutrition and reproduction, and can have unique features like multinucleation.
Secondary Endosymbiosis
When a eukaryotic cell engulfs another eukaryotic cell that has already undergone primary endosymbiosis, resulting in organelles like chloroplasts with multiple membranes.
Eukaryotic Cell
A complex cell type with a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, capable of engulfing other cells, leading to structures like chloroplasts through endosymbiosis.
Paraphyletic Group
A group of organisms that includes a common ancestor and some, but not all, of its descendants, often used for convenience in classification.
Monophyletic
A group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all its descendants, forming a single branch on the tree of life.
Unicellular
Organisms composed of a single cell, capable of performing all necessary life functions independently.
Colonial
Organisms that live together in a connected group, often sharing resources and sometimes exhibiting specialized roles, but each cell retains the ability to survive independently.
Multicellular
Organisms composed of multiple cells that differentiate and specialize to perform various functions, often arising independently in different evolutionary lineages.
Mitosis
A process where a single eukaryotic cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells, involving phases like prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Phylogenetic Tree
A branching diagram showing evolutionary relationships among species, indicating common ancestry and divergence points.
Cilia
Hair-like structures on eukaryotic cells that beat rhythmically to move fluid, mucus, or cells over their surface, or to propel the cell itself.
Flagella
Long, whip-like appendages used by cells for locomotion, often found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, but differing structurally between the two.