Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackProkaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells quiz
1/51
Terms in this set (51)
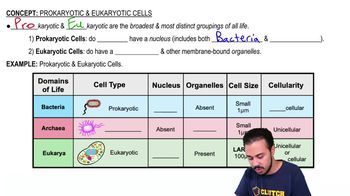
- What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their nucleus?Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus, whereas eukaryotic cells do have a nucleus.
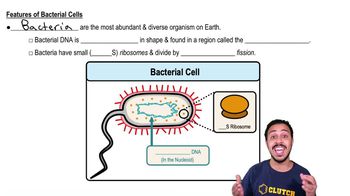
- How is the DNA of prokaryotic cells different from that of eukaryotic cells?Prokaryotic cells have circular DNA, while eukaryotic cells have linear DNA.
- Where is the DNA located in prokaryotic cells?In prokaryotic cells, DNA is located in a region called the nucleoid.
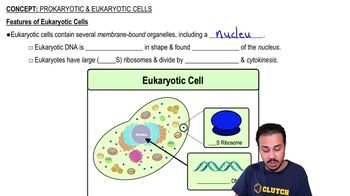
- What is the size difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes?Prokaryotic cells have 70S ribosomes, which are smaller, while eukaryotic cells have 80S ribosomes, which are larger.
- What process do prokaryotic cells use to divide?Prokaryotic cells divide by a process called binary fission.
- What type of cell division do eukaryotic cells undergo?Eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis and cytokinesis.
- Which type of cells are generally larger, prokaryotic or eukaryotic?Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells.
- Do prokaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles?No, prokaryotic cells do not have membrane-bound organelles.
- What are the small structures found in all cells that are responsible for protein synthesis?Ribosomes are the small structures found in all cells responsible for protein synthesis.
- What is the term for the process by which eukaryotic cells divide?The process by which eukaryotic cells divide is called mitosis and cytokinesis.
- What is the shape of eukaryotic DNA?Eukaryotic DNA is linear in shape.
- What is the term for the small ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells?The small ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells are called 70S ribosomes.
- What is the term for the larger ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells?The larger ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells are called 80S ribosomes.
- What is the main structural difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?The main structural difference is that prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have both.
- What is the term for the region where prokaryotic DNA is found?The region where prokaryotic DNA is found is called the nucleoid.
- which statement is most likely to apply to a cell that has dna within its cytoplasm?The cell is most likely a prokaryotic cell, as prokaryotic cells have circular DNA located in the cytoplasm within a region called the nucleoid.
- which structure is unique to eukaryotic cells? dna cell membrane ribosomes nucleusNucleus is unique to eukaryotic cells, as prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus.
- which cell structure serves the stated function in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?Ribosomes serve the function of protein synthesis in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
- which of the cells shown in the figure are eukaryotic cells?Eukaryotic cells are those that contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- which statement best distinguishes plant cells and animal cells?Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, while animal cells do not.
- which is a function of the cell structure that is labeled x?If 'X' is a nucleus, its function is to store the cell's genetic material and coordinate activities like growth and reproduction.
- which statement accurately compares cell division in bacterial and eukaryotic cells?Bacterial cells divide by binary fission, a simpler process, while eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis and cytokinesis, which is more complex.
- cells that contain only circular chromosomes are most probably which of the following?Cells with only circular chromosomes are most likely prokaryotic cells.
- looking at a cell under a microscope, you note that it is a prokaryote. how do you know?You know it's a prokaryote because it lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
- which structure is unique to eukaryotic cells?The nucleus is unique to eukaryotic cells.
- which type of cell is pictured on the right?Without the image, it's unclear, but if it has a nucleus, it's a eukaryotic cell; if not, it's a prokaryotic cell.
- the study of which structure was instrumental in the formulation of the modern cell theory?The study of the cell membrane and nucleus was instrumental in the formulation of the modern cell theory.
- which descriptions apply to prokaryotic cells? check all that apply.Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, have circular DNA, are unicellular, and divide by binary fission.
- which cell structures are seen in all cell types? check all that apply.All cell types have a cell membrane and ribosomes.
- which cell structures are seen in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes and a cell membrane.
- which of the following statements is part of the cell theory?All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
- which cellular component will be found in the widest range of organisms in the sample?Ribosomes will be found in the widest range of organisms, as they are present in all cell types.
- according to the cell theory, which describes cells?Cells are the basic unit of life, and all living organisms are composed of cells.
- which of the following makes bacteria and archaea different from eukaryotes?Bacteria and archaea lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, unlike eukaryotes.
- which of the following correctly describes the function of the cell wall?The cell wall provides shape, support, and resistance to osmotic pressure.
- what statement describes a cell?A cell is the smallest unit of life that can function independently and perform all necessary functions of life.
- which type(s) of cells have genetic material that is contained in a nucleus?Eukaryotic cells have genetic material contained in a nucleus.
- if you wanted to see a cell wall, where could you look?You could look at plant cells, fungi, and some prokaryotic cells like bacteria.
- which types of microorganisms have cells that do not contain organelles?Prokaryotic microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, have cells that do not contain organelles.
- which cell structure provides shape, support, and resistance to osmotic pressure?The cell wall provides shape, support, and resistance to osmotic pressure.
- what is the approximate diameter of the mature parent cell?Prokaryotic cells are about 1 micrometer in diameter, while eukaryotic cells can be 10 to 100 micrometers.
- which cell size is the most efficient at exchanging materials with the environment?Smaller cells are more efficient at exchanging materials with the environment due to a higher surface area-to-volume ratio.
- which of the following is not found in all cells?A nucleus is not found in all cells; it is absent in prokaryotic cells.
- which of these is not a difference between eukaryotic and bacterial gene expression?Both eukaryotic and bacterial cells use ribosomes for protein synthesis, so ribosome function is not a difference.
- in what way do the membranes of eukaryotic cells vary?Eukaryotic cell membranes vary in the presence of membrane-bound organelles.
- what three basic parts are found in most human cells?Most human cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a cell membrane.
- what are the two major parts of a eukaryotic cell?The two major parts of a eukaryotic cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
- which structures are common to both plant and animal cells?Both plant and animal cells have a nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and a cell membrane.
- who coined the term cell, in reference to the tiny structures seen in living organisms?Robert Hooke coined the term 'cell' when observing cork under a microscope.
- which is a key factor that limits the size of a cell?The surface area-to-volume ratio is a key factor that limits the size of a cell.
- what features are a part of all cells? select all that apply.All cells have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.