Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cells definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (18)
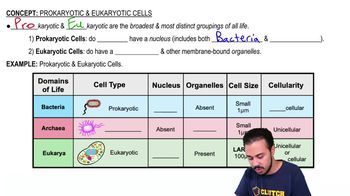
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms lacking a nucleus and organelles, classified into the domains Bacteria and Archaea.
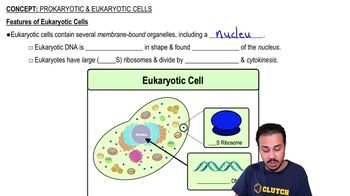
Nucleus
A membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that houses and protects the cell's genetic material (DNA), facilitating processes like replication and transcription.
Organelles
Specialized structures within eukaryotic cells that perform distinct processes, such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste management.
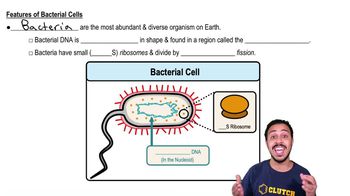
Bacteria
Single-celled prokaryotes without a nucleus or organelles, with DNA in a nucleoid region, often having a cell wall.
Archaea
A domain of single-celled prokaryotes distinct from bacteria, often found in extreme environments, lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Eukarya
Domain of life with organisms that have cells containing a nucleus and organelles; includes animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with cells that have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, which can be either unicellular or multicellular.
Fungi
Eukaryotic organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms; they decompose organic matter and reproduce via spores.
Protista
A diverse group of eukaryotic microorganisms, often unicellular, that do not fit into the other eukaryotic kingdoms (plants, animals, fungi).
Nucleoid
A region within prokaryotic cells where the DNA is located, not enclosed by a membrane, unlike the nucleus in eukaryotic cells.
Chromosomes
Threadlike structures composed of DNA and proteins, found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, carrying genetic information essential for inheritance and cell function.
Genetic Material
Molecule that carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms and many viruses.
Mitochondria
Organelle in eukaryotic cells that generates ATP through cellular respiration, often referred to as the "powerhouse" of the cell.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures that synthesize proteins by translating messenger RNA into polypeptide chains, found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Chloroplast
Organelle in eukaryotic cells where photosynthesis occurs, converting light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose.
Nucleolus
A dense region within the nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis and ribosome assembly occur.
Cell Wall
A rigid outer layer found in plant cells, bacteria, fungi, and some protists, providing structural support and protection.
Bacterium
A single-celled prokaryotic organism lacking a nucleus and organelles, with DNA located in a nucleoid region.