Prokaryote Reproduction and Gene Exchange exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
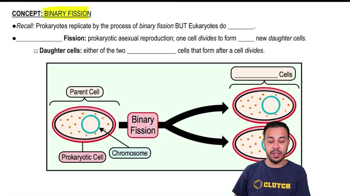
Binary Fission
Asexual reproduction in prokaryotes resulting in two identical daughter cells.
What is the exponential phase in bacterial growth?
A period where bacteria grow at an exponential rate due to optimal conditions and nutrients.
Mutation Rate in Prokaryotes
High mutation rates due to short generation times and large populations, leading to genetic variation.
Transformation
Process where a prokaryote takes up external DNA from its environment and incorporates it into its genome.
What is transduction?
The transfer of DNA from one bacterium to another via a virus.
Conjugation
Direct transfer of genetic material between two physically connected prokaryotic cells via a pilus.
F Plasmid
A plasmid that carries genes required for the formation of a pilus and gene transfer during conjugation.
What is an R plasmid?
A plasmid that carries genes conferring antibiotic resistance.
Exponential Growth
Rapid increase in bacterial population when conditions are optimal.
What is the role of a pilus in conjugation?
A pilus connects two bacterial cells, allowing the transfer of genetic material.
Genetic Variation in Prokaryotes
Achieved through mutation, transformation, transduction, and conjugation.
What is the F factor?
A genetic element that includes the F plasmid and genes incorporated into the bacterial chromosome.
Antibiotic Resistance
The ability of bacteria to survive and proliferate despite the presence of antibiotics, often due to R plasmids.
What is the significance of short generation times in bacteria?
They contribute to high mutation rates and rapid evolution.
Transfection
The process of introducing DNA into eukaryotic cells via a virus.
What happens during the stationary phase of bacterial growth?
Bacterial growth levels off due to nutrient depletion or space limitations.
Bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria and can transfer DNA between bacterial cells.
What is the role of a donor cell in conjugation?
A cell that possesses the F factor and transfers genetic material to a recipient cell.
Plasmid
A small, circular piece of DNA in bacteria that can replicate independently of chromosomal DNA.
What is the significance of genetic exchange in prokaryotes?
It enhances genetic diversity, aiding in adaptation and evolution.
Exogenous DNA
DNA that originates outside the cell and can be incorporated into the cell's genome.
What is the difference between F+ and F- bacteria?
F+ bacteria have the F plasmid, while F- bacteria lack it and act as recipients in conjugation.
Vector
An agent, such as a virus, that transfers genetic material from one organism to another.
What is the role of a recipient cell in conjugation?
A cell that lacks the F factor and receives genetic material from a donor cell.
Chromosomal DNA
The main genetic material in a cell, containing most of the organism's genes.
What is the role of bacteriophages in transduction?
They transfer DNA from one bacterial cell to another, introducing genetic variation.
Generation Time
The time it takes for a bacterial population to double in number.
What is the significance of the F prime bacteria?
Bacteria with the F factor incorporated into their chromosomal DNA, capable of gene transfer.
Capsid
The protein shell of a virus that encases its genetic material.