Prokaryote Cell Structures quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackProkaryote Cell Structures quiz
1/23
Terms in this set (23)
- What is the function of the capsule in prokaryotic cells?The capsule, also known as the slime layer, is a large polysaccharide coating that provides an additional protective layer for the cell.
- What are endospores and why do some bacteria form them?Endospores are super resilient, dormant forms of bacteria that form in response to harsh conditions or a lack of nutrients.
- How do fimbriae help prokaryotic cells?Fimbriae are appendages that allow bacterial cells to adhere to surfaces.
- What is the role of flagella in prokaryotic cells?Flagella are whip-like appendages used for locomotion and sensation in prokaryotic cells.
- What is the function of the pilus in bacterial cells?The pilus, or sex pilus, is involved in conjugation, allowing bacteria to pass DNA between cells.
- What percentage of Earth's biomass is made up of prokaryotic cells?Prokaryotic cells make up 60% of Earth's biomass.
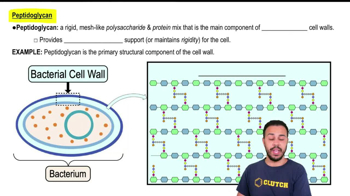
- What is the main difference between the cell walls of archaea and bacteria?Unlike bacteria, archaea do not use peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
- What is binary fission?Binary fission is an asexual reproduction process where one cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
- How does transformation introduce genetic variation in prokaryotes?Transformation occurs when a prokaryotic cell incorporates exogenous DNA from the environment into its genome.
- What is transduction in the context of prokaryotic genetic variation?Transduction is the process where DNA is transferred from one bacterial cell to another by a virus.
- What are extremophiles and which domain do they belong to?Extremophiles are organisms that thrive in extreme environments, and many belong to the domain Archaea.
- What is the significance of methanogens in the environment?Methanogens produce methane as a byproduct of their metabolism and are found in environments like swamps and the guts of animals.
- What is the main structural difference in the phospholipids of hot spring archaea compared to other prokaryotes?The phospholipids of hot spring archaea are made of isoprene units, which allow their membranes to resist breaking down at high temperatures.
- What is the role of bacteriophages in genetic variation of prokaryotes?Bacteriophages can transfer bacterial DNA between cells, introducing genetic variation through a process called transduction.
- How do archaea differ from bacteria in terms of genetic machinery?The genetic machinery for transcription and translation in archaea is more similar to eukaryotes than to bacteria.
- which of the following are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface?Fimbriae are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface.
- how does a capsule help certain bacteria evade detection by the immune system?A capsule helps bacteria evade detection by the immune system by providing a dense, organized layer that can mask antigens and prevent phagocytosis.
- which of the following apply to bacterial smears?Bacterial smears are used to prepare bacteria for staining and microscopic examination, allowing for the observation of cell shape, arrangement, and Gram reaction.
- _____ are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface.Fimbriae are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface.
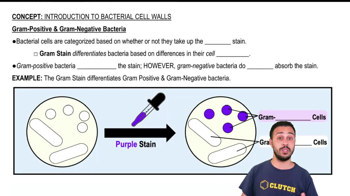
- which of the following are true statements describing the gram-negative outer membrane?The gram-negative outer membrane is a complex structure that contains lipopolysaccharides and provides an additional barrier to certain antibiotics and detergents.
- the dna-containing region of this bacterial cell is indicated by the letter _____.The DNA-containing region of a bacterial cell is indicated by the letter 'N' for nucleoid.
- what is a function of a bacterium's capsule?A function of a bacterium's capsule is to protect the cell from desiccation and phagocytosis, aiding in survival and virulence.
- which of the following is a component of gram-negative cells but not gram-positive cells?The outer membrane is a component of gram-negative cells but not gram-positive cells.