Prokaryote Cell Structures definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (12)
Bacteria
Microscopic, single-celled prokaryotes lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, with a cell wall made of peptidoglycan, found in diverse environments and essential to Earth's biomass.
Nucleus
The central organelle in eukaryotic cells that houses genetic material (DNA) and coordinates activities like growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
Nucleoid
A dense, irregularly-shaped region within prokaryotic cells where the majority of the cell's genetic material (DNA) is located, lacking a surrounding membrane.
Plasmids
Small, circular DNA molecules in prokaryotes, separate from chromosomal DNA, often carrying genes beneficial for survival, such as antibiotic resistance.
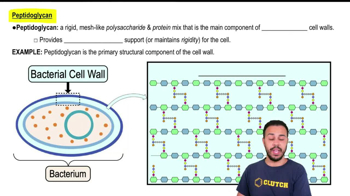
Peptidoglycan
A structural polymer in bacterial cell walls, composed of sugar chains cross-linked by short peptides, providing rigidity and shape to the cell.
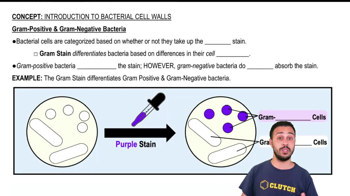
Gram Stain
A differential staining technique that classifies bacteria based on cell wall composition, distinguishing between those with thick peptidoglycan layers (positive) and those with thin layers and outer membranes (negative).
Lipopolysaccharides
A molecule in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria, composed of lipid and polysaccharide, crucial for structural integrity and triggering immune responses.
Capsule
A polysaccharide layer surrounding some prokaryotic cells, providing protection and aiding in adherence to surfaces.
Endospores
Dormant, highly resilient bacterial forms that develop in response to nutrient scarcity or harsh conditions, enabling survival for extended periods, even centuries, until favorable conditions return.
Fimbria
Hair-like appendages on prokaryotic cells that enable them to adhere to surfaces, facilitating attachment and colonization.
Flagella
Whip-like appendages used by prokaryotic cells for locomotion and sensory functions, enabling movement through mediums like water by rotating in a propeller-like fashion.
Pilus
A surface appendage on many bacterial cells that facilitates DNA transfer between cells during conjugation, acting as a bridge for genetic exchange.