Plant Development quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackPlant Development quiz
1/17
Terms in this set (17)
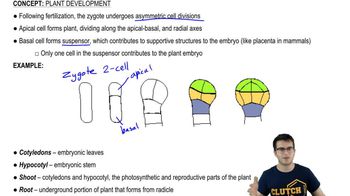
- What are the two cells formed after the asymmetric division of a plant zygote called?The two cells are called the apical cell and the basal cell.
- What structure does the basal cell form in plant development?The basal cell forms the suspensor, which contributes to the supportive structures of the embryo.
- What is the role of the shoot apical meristem (SAM) in plant development?The shoot apical meristem gives rise to organs like flowers and leaves.
- What are cotyledons in the context of plant development?Cotyledons are embryonic leaves in the developing plant embryo.
- What is the function of the root apical meristem (RAM)?The root apical meristem gives rise to the roots of the plant.
- What are the three embryonic tissues formed along the radial axis in plant development?The three embryonic tissues are the epidermis, ground tissue, and vascular tissue.
- What is the primary function of the epidermis in plants?The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells specialized to protect the organism.
- What is the role of ground tissue in plants?Ground tissue differentiates into specialized cells like photosynthetic cells.
- What are xylem and phloem, and from which tissue do they arise?Xylem and phloem are types of vascular tissues that arise from the vascular tissue.
- What hormone provides positional information in developing plants?The hormone auxin provides positional information in developing plants.
- What is the major difference between plant and animal cells in terms of cell fate?Unlike animal cells, some plant cells can dedifferentiate to become different types of cells.
- What is the significance of the ability of plant cells to dedifferentiate?This ability allows humans to cultivate plants from clippings, as plant cells can become different types of cells.
- What is the hypocotyl in plant development?The hypocotyl is the embryonic stem of the developing plant.
- What is the function of the meristem in plants?The meristem contains plant stem cells that can give rise to various structures like roots, leaves, and new stalks.
- What is the role of the suspensor in plant embryos?The suspensor contributes to the supportive structures of the embryo, similar to the placenta in mammals.
- secondary growth never occurs in _____.Secondary growth never occurs in herbaceous plants. These plants do not develop the woody tissues that are characteristic of secondary growth, which is more common in woody plants like trees and shrubs.
- _____ is a better explanation for how chromosomes were added in plants, rather than in animals.Polyploidy is a better explanation for how chromosomes were added in plants, rather than in animals. This process involves the duplication of the entire set of chromosomes, which is more common in plants and can lead to increased genetic diversity and adaptation.