Phototropism quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
What is phototropism?
Phototropism is the growth of a plant toward or away from light.
What are photoreceptors and why are they important in phototropism?
Photoreceptors are proteins that respond to light, and they are essential for plants to detect light and direct their growth accordingly.
What is the role of blue light in phototropism?
Blue light is a high-energy light that is crucial for photosynthesis and also plays a significant role in phototropism by being detected by phototropins.
How do plants use far red light to detect shade?
Far red light passes through leaves and helps plants detect shade, indicating that they are not receiving optimal sunlight for photosynthesis.
What is the red far red switch in plants?
The red far red switch is a mechanism where phytochromes change conformation in response to red and far red light, helping plants detect light and shade.
What is etiolation and how do plants respond to the absence of sunlight?
Etiolation is the response of plants to the absence of sunlight, which includes growing longer internodes and experiencing chlorosis to conserve energy.
What is photomorphogenesis?
Photomorphogenesis is the growth and development of plants in response to different spectrums of light.
What are phytochromes and their role in phototropism?
Phytochromes are photoreversible photoreceptors that detect red and far red light, playing a key role in phototropism and shade avoidance.
How do plants use circadian rhythms to optimize their growth?
Plants use circadian rhythms to regulate daily cycles, such as hormone concentration and turgidity, to maximize photosynthesis and protect against environmental conditions.
What is vernalization and its significance in plant blooming?
Vernalization is a cold pretreatment required for some plants to bloom, ensuring they have passed through winter and will bloom in the appropriate season.
What is the hypothetical hormone that induces flowering in plants?
The hypothetical hormone that induces flowering in plants is called florigen.
- What is the role of auxin in phototropism?Auxin is a plant hormone that causes cells on the shade side of a plant to elongate, resulting in the plant bending towards the light source.
- What is the chemical name of auxin?The chemical name of auxin is indoleacetic acid.
- What is the Colin D. Wendt hypothesis?The Colin D. Wendt hypothesis states that auxin moves from the light side to the shade side of a plant, causing asymmetric growth and bending towards the light.
- How do proton pumps contribute to the acid growth hypothesis?Proton pumps increase the concentration of protons in the cell wall, which loosens hydrogen bonds in cellulose, allowing water to enter and causing cell elongation.
- What are expansins and their role in cell elongation?Expansins are proteins that loosen hydrogen bonds in cellulose, allowing water to enter the cell wall and facilitating cell elongation.
- What is polar transport of auxin?Polar transport of auxin refers to its unidirectional movement from the shoots to the roots, regardless of gravity.
- What is photomorphogenesis?Photomorphogenesis is plant growth in response to different spectrums of light.
- What are phototropins and their function?Phototropins are blue light photoreceptors that help plants detect light for phototropism and other processes like stomata opening.
- What is the role of phytochromes in plant responses to light?Phytochromes are photoreceptors that detect red and far-red light, playing a role in processes like seed germination and shade avoidance.
- What is the red far-red switch?The red far-red switch is a mechanism where phytochromes change conformation in response to red and far-red light, helping plants detect light and shade.
- What is etiolation and its symptoms?Etiolation is the response of plants to the absence of sunlight, characterized by longer internodes and chlorosis (lack of chlorophyll).
- What is the significance of far-red light for plants?Far-red light indicates shade and triggers responses like stem elongation and branching to help plants reach direct sunlight.
- What is the function of aquaporins in plant cells?Aquaporins are channels that facilitate the movement of water into plant cells, aiding in cell elongation.
- How does auxin influence apical dominance?Auxin maintains apical dominance by promoting the growth of the central stem over lateral stems, ensuring the plant grows towards light.
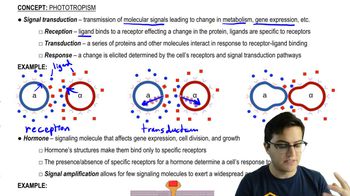
- What is the role of signal transduction in plant responses?Signal transduction involves the reception, transduction, and response to molecular signals, leading to changes in metabolism, gene expression, or growth.
- what caused the shoots of the seedlings on the windowsill to bend toward the window?The bending of the seedlings' shoots toward the window is caused by phototropism, a process where plants grow towards a light source. This is facilitated by the hormone auxin, which redistributes to the shaded side of the plant, causing those cells to elongate more than the cells on the light-exposed side. This differential growth results in the plant bending towards the light.