Phototropism exam Flashcards
 Back
BackPhototropism exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- PhototropismGrowth of a plant towards or away from light.
- What is the role of auxin in phototropism?Auxin facilitates growth towards light by creating asymmetric growth patterns.
- PhytochromesPhotoreceptors that detect red and far-red light, influencing processes like flowering and circadian rhythms.
- How do plants detect light?Plants use photoreceptors such as phytochromes and cryptochromes to detect light wavelengths.
- PhotomorphogenesisPlant growth in response to different spectrums of light.
- What is the acid growth hypothesis?It explains how auxin causes cell elongation by pumping protons into the cell wall, allowing water to enter and expand the cell.
- EtiolationPlant responses to the absence of sunlight, such as growing towards the sun and having longer internodes.
- What is the function of cryptochromes?Photoreceptors that detect blue light and influence circadian rhythms in plants.
- PhototropinsBlue light photoreceptors involved in phototropism and stomata opening and closing.
- What is the role of phytochromes in shade avoidance?Phytochromes detect far-red light, causing plants to lengthen stems or induce branching to grow into direct light.
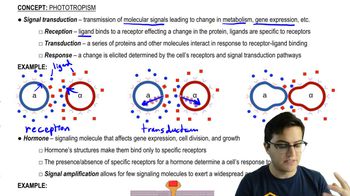
- Signal TransductionThe process by which a signal is carried through the cell, leading to a response.
- What is the Colin D. Wendt hypothesis?It states that auxin moves from the light side to the shade side of the plant, causing asymmetric growth.
- PhotoperiodismPhysiological responses of plants to the lengths of day and night.
- What is vernalization?A pretreatment with cold necessary for some plants to bloom in response to photoperiod.
- FlorigenThe hypothetical hormone believed to induce flowering in plants.
- What is the role of second messengers in signal transduction?Intracellular signaling molecules that carry the signal within the cell.
- ChlorosisA lack of chlorophyll in plants, often due to an absence of sunlight.
- What is the function of expansins?Proteins that loosen hydrogen bonds in cellulose, allowing water to enter the cell wall.
- Circadian RhythmsDaily cycles in plants that influence hormone concentration and other physiological processes.
- What is the red-far red switch?A mechanism where phytochromes switch between forms in response to red and far-red light, helping plants detect light and shade.
- AuxinA plant hormone responsible for growth towards light and other functions.
- What is the role of photoreceptors in phototropism?Photoreceptors detect light and initiate the growth response towards or away from it.
- PhyllotaxyThe arrangement of leaves on a stem.
- What is the role of hormones in plant signaling?Hormones affect gene expression, cell division, and growth, mediating plant responses to environmental stimuli.
- Apical DominanceThe phenomenon where the central stem of the plant is dominant over other side stems.
- What is the function of proton pumps in the acid growth hypothesis?Proton pumps concentrate protons in the cell wall, leading to water entry and cell elongation.
- PhotoreceptorsProteins that respond to light and initiate plant responses.
- What is the role of blue light in phototropism?Blue light is detected by phototropins and is crucial for phototropism and photosynthesis.
- Signal AmplificationA process where a few signaling molecules have a large effect, amplifying the signal.