Phototropism definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (10)
Photoreceptors
Cells in plants that detect light and initiate growth responses, such as bending towards light, by interacting with hormones like auxin.
Auxin
A plant hormone, indoleacetic acid, that regulates growth by promoting cell elongation, especially in response to light, causing plants to bend towards light sources.
Indoleacetic Acid
It is the chemical name of auxin.
Colin D. Wendt Hypothesis
The hypothesis posits that auxin, a plant hormone, moves from the light-exposed side to the shaded side of a plant, causing cells on the shaded side to elongate more, resulting in the plant bending towards the light.
Acid Growth Hypothesis
Plant cells elongate by pumping protons into the cell wall, loosening it and allowing water influx, driven by auxin, leading to cell expansion and growth towards light.
Proton Pumps
Membrane proteins that transport protons (H⁺ ions) out of cells, creating an electrochemical gradient that facilitates various cellular processes, including nutrient uptake and cell elongation.
Aquaporins
Proteins that form channels in cell membranes, facilitating rapid water transport in and out of cells, crucial for maintaining cellular water balance and enabling processes like plant cell elongation.
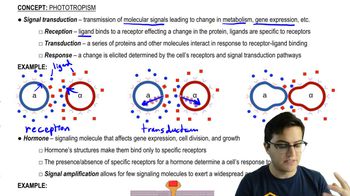
Signal Transduction
The process by which a cell converts an external signal into a functional response, involving reception, transduction, and cellular response, often through a cascade of molecular interactions.
Ligand
A molecule that binds to a specific receptor to initiate a cellular response, often involved in signal transduction pathways.
Phosphorylation Cascades
A series of protein activations and deactivations through phosphate group transfers, amplifying cellular signals and leading to specific cellular responses.