Photorespiration quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (13)
What is photorespiration and why do plants want to avoid it?
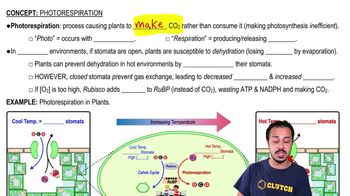
Photorespiration is a process that wastes ATP and NADPH and produces carbon dioxide, causing the plant to lose carbon. Plants want to avoid it because it is inefficient compared to the Calvin cycle, which produces glucose.
Under what conditions is photorespiration more likely to occur?
Photorespiration is more likely to occur when the stomata are closed and oxygen gas concentrations within the plant are high.
What happens when the stomata are open and carbon dioxide concentrations are high?
When the stomata are open and carbon dioxide concentrations are high, the Calvin cycle occurs as Rubisco binds carbon dioxide with RuBP to produce glucose.
Why is high oxygen concentration within the plant a problem for the Calvin cycle?
High oxygen concentration is a problem because Rubisco may bind oxygen instead of carbon dioxide, leading to photorespiration instead of the Calvin cycle.
What role does Rubisco play in the Calvin cycle?
Rubisco binds carbon dioxide with RuBP to initiate the Calvin cycle, leading to the production of glucose.
What is the consequence of the stomata remaining closed for gas exchange?
When the stomata remain closed, oxygen cannot leave and carbon dioxide cannot enter, leading to increased oxygen concentration and the likelihood of photorespiration.
How does photorespiration affect the plant's energy resources?
Photorespiration wastes ATP and NADPH, which are crucial for the plant's energy and metabolic processes.
What is the primary product of the Calvin cycle?
The primary product of the Calvin cycle is glucose.
Why does Rubisco sometimes bind to oxygen instead of carbon dioxide?
Rubisco binds to oxygen instead of carbon dioxide when oxygen concentrations are high and carbon dioxide concentrations are low, leading to photorespiration.
What is the initial step of the Calvin cycle?
The initial step of the Calvin cycle is the binding of carbon dioxide to RuBP by the enzyme Rubisco.
What happens to the oxygen produced during the light reactions when the stomata are closed?
When the stomata are closed, the oxygen produced during the light reactions cannot leave the plant, leading to increased internal oxygen concentration.
What is the relationship between photorespiration and the Calvin cycle?
Photorespiration and the Calvin cycle are competing processes; photorespiration is wasteful, while the Calvin cycle is productive in terms of glucose synthesis.
How does the closure of stomata affect carbon dioxide availability for the Calvin cycle?
The closure of stomata reduces carbon dioxide availability, hindering the Calvin cycle and increasing the likelihood of photorespiration.