Osmosis exam Flashcards
 Back
BackOsmosis exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
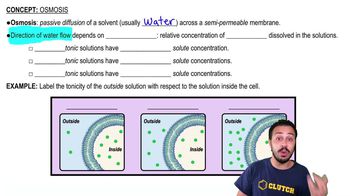
- OsmosisThe passive diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane.
- TonicityThe relative concentration of solutes in a solution compared to another solution.
- What is a hypotonic solution?A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to another solution.
- IsotonicA solution with equal solute concentration compared to another solution.
- What happens to animal cells in a hypotonic environment?They may lyse (burst) due to water influx.
- HypertonicA solution with a higher solute concentration compared to another solution.
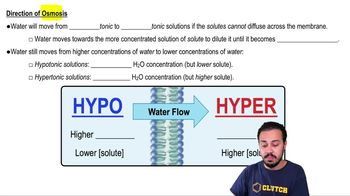
- What is the direction of water movement in osmosis?From hypotonic solutions towards hypertonic solutions.
- CrenationThe process where animal cells shrink due to water loss in a hypertonic environment.
- PlasmolysisThe process where plant cells shrink due to water loss in a hypertonic environment.
- What is turgor pressure?The pressure of water inside the cell against the cell wall in plant cells.
- What happens to plant cells in a hypotonic environment?They thrive due to increased turgor pressure.
- What is the preferred environment for animal cells?Isotonic environments.
- What is the preferred environment for plant cells?Hypotonic environments.
- What happens to cells in an isotonic environment?Water enters and exits the cell at equal rates, and the cell size remains unchanged.
- What is the solvent in biological systems?Water.
- What is the effect of a hypertonic environment on cells?Cells lose water and shrink.
- What is the effect of a hypotonic environment on animal cells?Cells may swell and burst (lyse).
- What is the effect of a hypotonic environment on plant cells?Cells swell but do not burst due to the cell wall, increasing turgor pressure.
- What is the effect of an isotonic environment on plant cells?Cells survive but do not have maximum turgor pressure.
- What is the effect of a hypertonic environment on plant cells?Cells undergo plasmolysis and may wilt.
- What is the main driving force of osmosis?The difference in solute concentration across a semi-permeable membrane.
- What is the main difference between solute and solvent?Solute is the substance being dissolved, while solvent is the substance doing the dissolving.
- What happens to water concentration in a hypotonic solution?It is higher compared to a hypertonic solution.
- What happens to water concentration in a hypertonic solution?It is lower compared to a hypotonic solution.
- What is the role of the cell wall in plant cells during osmosis?It prevents over-expansion and bursting in hypotonic environments.
- What is the analogy used to describe cell swelling in a hypotonic environment?A balloon expanding as air flows into it.
- What is the analogy used to describe cell shrinking in a hypertonic environment?A balloon shrinking as air exits it.
- What is the analogy used to remember the effect of a hypotonic environment on cells?Cells swell up like a hippo.
- What is the analogy used to remember the effect of a hypertonic environment on cells?Cells dehydrate like a hyper kid.