Non-Random Mating exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (25)
Non-random mating
Occurs when certain genotypes are more likely to mate, affecting genotype frequencies without altering allele frequencies.
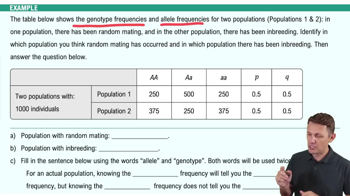
What is inbreeding?
A form of non-random mating that increases homozygosity by mating between relatives.
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
A principle stating that allele and genotype frequencies in a population will remain constant in the absence of evolutionary influences.
Does non-random mating cause evolution?
No, it affects genotype frequencies but does not alter allele frequencies, thus not causing evolution.
Inbreeding depression
A reduction in fitness due to the expression of deleterious recessive alleles in homozygous individuals.
What is homozygosity?
A measure of how many homozygotes are present in a population.
Sexual selection
A form of natural selection where certain traits increase an individual's chances of mating.
How does non-random mating affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
It disrupts Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium by altering genotype frequencies.
Deleterious recessive alleles
Harmful alleles that can cause a decrease in fitness when expressed in a homozygous state.
What is required for allele frequencies to change?
Natural selection is required to change allele frequencies and drive evolutionary change.
Proximity
A factor that often leads to non-random mating as organisms are more likely to mate with those nearby.
What is the effect of inbreeding on homozygosity?
Increases homozygosity in the population.
Wind pollination
A seemingly random process where pollen is distributed by the wind, but still limited by distance.
How does inbreeding lead to inbreeding depression?
By increasing the likelihood of homozygous deleterious recessive alleles, reducing fitness.
Genotype frequencies
The proportion of different genotypes in a population.
What is the misconception about non-random mating?
It is not the same as sexual selection; non-random mating assumes all alleles are passed on, just not randomly paired.
Fitness
The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce, passing on its genes to the next generation.
What happens to rare recessive alleles in inbreeding?
They are more likely to be paired together, exposing deleterious phenotypes.
Natural selection
The process where organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
How does non-random mating affect allele frequencies?
It does not affect allele frequencies directly; natural selection is needed for that.
Population dynamics
The study of how and why populations change over time.
What is the role of natural selection in non-random mating?
Natural selection can act on the increased homozygosity to change allele frequencies and drive evolution.
What is the main assumption of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
Random mating among individuals in the population.
How does proximity influence non-random mating?
Organisms are more likely to mate with those that are geographically closer.
What is the effect of non-random mating on a population?
It pushes the population out of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium by altering genotype frequencies.