Neurons and Action Potentials exam Flashcards
 Back
BackNeurons and Action Potentials exam
1/30
Terms in this set (30)
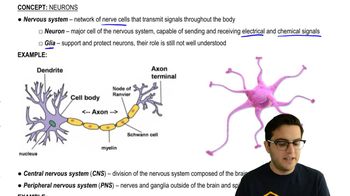
- NeuronA nerve cell that transmits electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system.
- What is the role of glial cells?Glial cells support and protect neurons.
- AxonA long projection of a neuron that transmits electrical signals to the terminal.
- What is the function of dendrites?Dendrites receive signals from other neurons.
- Action PotentialA rapid rise and fall in membrane potential that propagates along the axon.
- What is the role of myelin sheaths?Myelin sheaths insulate axons and speed up action potential propagation.
- Nodes of RanvierGaps in the myelin sheath where ion channels are concentrated.
- What is a synapse?A junction between two neurons where signals are transmitted.
- NeurotransmitterChemical messengers that transmit signals across a synapse.
- What is acetylcholine?A neurotransmitter involved in muscle contraction and other functions.
- GABAGamma-aminobutyric acid, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS.
- What is depolarization?A decrease in membrane potential, making the inside of the cell less negative.
- RepolarizationThe process of restoring the resting membrane potential after depolarization.
- What is hyperpolarization?An increase in membrane potential, making the inside of the cell more negative.
- Central Nervous System (CNS)Comprises the brain and spinal cord.
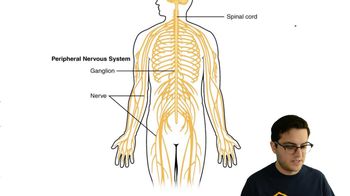
- What is the peripheral nervous system?The part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord.
- Sensory NeuronsNeurons that transmit sensory information to the CNS.
- What are motor neurons?Neurons that transmit signals from the CNS to muscles and glands.
- InterneuronsNeurons that transmit signals between other neurons.
- What is the resting membrane potential?The baseline membrane potential of a cell, typically negative.
- Voltage-Gated Ion ChannelsIon channels that open or close in response to changes in membrane potential.
- What are ligand-gated ion channels?Ion channels that open in response to the binding of a chemical messenger.
- Sodium-Potassium PumpA pump that uses ATP to move sodium out of the cell and potassium into the cell.
- What is an equilibrium potential?The membrane potential at which there is no net movement of a specific ion.
- Saltatory ConductionThe process by which action potentials jump from one node of Ranvier to the next.
- What is an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)?A depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that increases the likelihood of an action potential.
- Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP)A hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane that decreases the likelihood of an action potential.
- What is temporal summation?The process by which multiple postsynaptic potentials occurring in quick succession add together.
- Spatial SummationThe process by which multiple postsynaptic potentials occurring simultaneously at different locations add together.
- What is the role of calcium ions in neurotransmitter release?Calcium ions trigger the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane, releasing neurotransmitters.