Mutations exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
Mutation
A permanent change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
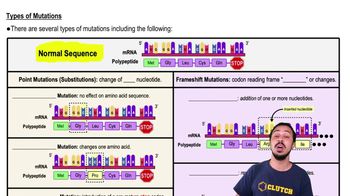
What is a point mutation?
A mutation involving the change of just one single nucleotide in the DNA.
Silent Mutation
A type of point mutation that does not alter the amino acid sequence.
What is a missense mutation?
A point mutation that changes one amino acid in the protein sequence.
Nonsense Mutation
A point mutation that introduces a premature stop codon.
What is a frameshift mutation?
A mutation caused by insertions or deletions that shift the reading frame of the codons.
Insertion Mutation
A type of frameshift mutation where one or more nucleotides are added to the DNA sequence.
Deletion Mutation
A type of frameshift mutation where one or more nucleotides are removed from the DNA sequence.
How do mutations impact RNA and protein synthesis?
Mutations in DNA can lead to changes in RNA via transcription and changes in proteins via translation.
Mutagen
Chemical agents that can induce mutations.
What is the impact of silent mutations on the amino acid sequence?
Silent mutations have no effect on the amino acid sequence.
How do missense mutations affect proteins?
They change one amino acid in the protein sequence.
How do frameshift mutations affect downstream amino acids?
They can change all downstream amino acids by shifting the reading frame.
What is the result of an insertion mutation?
The addition of nucleotides changes the reading frame of the codons.
What happens in a deletion mutation?
The removal of nucleotides changes the reading frame of the codons.
How can mutations be beneficial?
They can improve the chances of an organism's survival.
What are the three types of point mutations?
Silent, missense, and nonsense mutations.
How can mutations be harmful?
They can reduce the chances of an organism's survival.
What is the role of mutations in genetic diversity?
Mutations are largely responsible for the tremendous diversity among living organisms.
How can mutations be neutral?
They do not have an impact on the organism's survival.
What is the difference between point mutations and frameshift mutations?
Point mutations change one nucleotide without altering the reading frame, while frameshift mutations shift the reading frame.
How do environmental factors induce mutations?
Through exposure to mutagens, which are chemical agents that cause mutations.
What is the impact of a premature stop codon in a nonsense mutation?
It prematurely cuts the amino acid chain short.
How do natural processes cause mutations?
Mutations can occur naturally through processes within the cell.
What is the significance of mutations in evolution?
Mutations contribute to genetic variation, which is essential for evolution.
How does a silent mutation differ from a missense mutation?
A silent mutation does not change the amino acid sequence, while a missense mutation changes one amino acid.
What is the effect of a frameshift mutation caused by deletion?
It changes the reading frame and can alter all downstream amino acids.