Back
BackMutations definitions
Terms in this set (10)
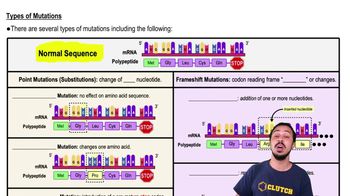
Nonsense Mutation
A mutation that converts a codon into a stop codon, leading to premature termination of protein synthesis and resulting in a nonfunctional protein.
Missense Mutation
A mutation that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in a protein, potentially altering its function.
Polypeptide Chain
A sequence of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, forming the primary structure of a protein.
Stop Codon
A codon that signals the end of translation, leading to the release of the newly synthesized polypeptide chain from the ribosome.
Nucleotide
A molecule composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups, forming the basic building block of nucleic acids like DNA and RNA.
Protein
A complex molecule composed of amino acids linked in a specific sequence, essential for cellular structure, function, and regulation.
mRNA
A molecule that carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where it specifies the amino acid sequence of the protein products.
Silent Mutation
A genetic mutation where a nucleotide change does not alter the amino acid sequence of the resulting protein, thus having no effect on its function.
Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides in mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or a termination signal during protein synthesis.
Amino Acid
Organic molecules that are the building blocks of proteins, each containing an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a unique side chain.