Microscopes definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (13)
Microscope
An optical instrument that magnifies tiny objects, such as cells, using visible light or electrons, enabling visualization beyond the capability of the human eye.
Optical Scope
An instrument that uses visible light to magnify and visualize microscopically small objects, such as cells, making them appear larger for detailed study.
Cells
The smallest unit of life, capable of performing all essential life processes, often requiring a microscope to be seen.
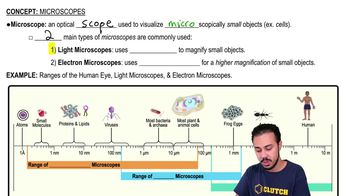
Light Microscopes
Optical instruments using visible light to magnify small objects, commonly used in biology labs to view cells and microorganisms.
Electron Microscopes
A microscope that uses electron beams to achieve high magnification, allowing visualization of structures as small as viruses, proteins, and even individual atoms.
Visible Light
The portion of the electromagnetic spectrum detectable by the human eye, ranging from approximately 400 to 700 nanometers in wavelength.
Magnification
The process of enlarging the appearance of an object using optical instruments, making tiny details visible to the human eye.
Human Eye
A complex organ that detects light and converts it into electrochemical signals, enabling vision by processing images and colors. It has a limited range for seeing microscopic objects.
Atom
The smallest unit of matter, consisting of a nucleus surrounded by electrons, fundamental to chemical elements and reactions.
Angstrom
A unit of length equal to 0.1 nanometers, often used to measure atomic and molecular scales.
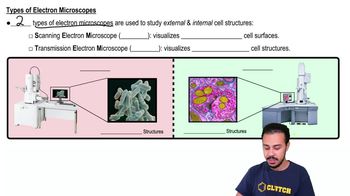
Transmission Electron Microscopes
A microscope that uses electron beams to visualize internal cell structures at very high magnifications, revealing details as small as individual molecules.
Scanning Electron Microscopes
A type of electron microscope that scans a sample with a focused beam of electrons to produce detailed 3D images of its surface.
External Features
Visible characteristics of an organism or cell, such as shape, size, and surface structures, observable without magnification or with minimal magnification.