Mendel's Laws definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (18)
Laws
Fundamental principles of genetics proposed by Mendel, including the separation of alleles during gamete formation and the independent assortment of genes, both occurring during meiosis.
Genetics
The study of heredity and variation in organisms, focusing on how traits are passed from parents to offspring through genes, governed by Mendel's laws of segregation and independent assortment.
Law Of Segregation
During gamete formation, two alleles for a gene separate randomly into different gametes, ensuring offspring inherit one allele from each parent.
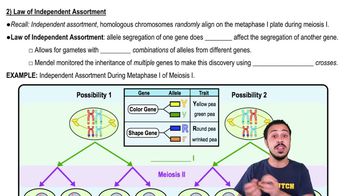
Law Of Independent Assortment
Genes for different traits segregate independently during gamete formation, due to the random alignment of homologous chromosome pairs in metaphase I of meiosis.
Meiosis
A type of cell division that produces four genetically distinct haploid cells, crucial for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
Alleles
Variants of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome, influencing specific traits.
Gamete
Formation The process where alleles segregate into different gametes during meiosis, ensuring genetic diversity through the separation of homologous chromosomes and independent assortment.
Cell Divison
The process by which a single cell divides to produce two or more daughter cells, ensuring genetic material is accurately replicated and distributed.
Homologous Chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes, one from each parent, with the same genes but possibly different alleles, that align and separate during meiosis.
Chromosome
A structure composed of DNA and proteins, found in the nucleus, that carries genetic information in the form of genes.
Anaphase I
The phase in meiosis where homologous chromosomes are separated, leading to the segregation of maternal and paternal alleles into different gametes.
Maternal Alleles
Alleles inherited from the mother, located on the homologous chromosomes she contributed, which segregate into different gametes during meiosis.
Paternal Alleles
Alleles inherited from the father, which segregate into different gametes during meiosis, following Mendel's law of segregation.
Synapsis
The pairing of homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis, facilitating genetic recombination through crossing over.
Crossing Over
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during prophase I of meiosis, leading to genetic variation in gametes.
Genetic Material
The molecular substance that carries genetic information, enabling inheritance and guiding cellular functions, through sequences of nucleotides.
Metaphase
The phase of meiosis where chromosomes align at the cell's equator, ensuring random and independent assortment of homologous chromosomes.
Cytokinesis
The process where the cytoplasm of a parent cell divides, resulting in two daughter cells, typically occurring after mitosis or meiosis.