Mendel's Experiments definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (24)
Gregor Mendel
A 19th-century scientist whose pea plant experiments established foundational principles of heredity, distinguishing between true breeding and hybrid plants through self and cross-fertilization.
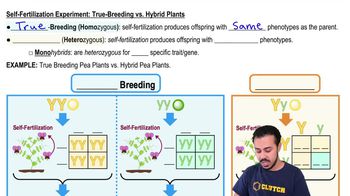
Self Fertilization
Fertilization where an organism uses its own pollen or sperm to fertilize its own ovules or eggs, resulting in offspring genetically similar to the parent.
True Breeding
Organisms that, when self-fertilized, produce offspring with the same phenotype as the parent, indicating homozygosity for the trait.
Hybrid
An organism resulting from the crossbreeding of two genetically distinct parents, often heterozygous, producing offspring with varied phenotypes.
Homozygous
Having identical alleles for a specific gene, resulting in a uniform phenotype upon self-fertilization.
Phenotype
Observable traits of an organism resulting from the interaction of its genetic makeup and environmental influences.
Heterozygous
An organism with two different alleles for a specific gene, resulting in a dominant and a recessive allele pairing.
Monohybrids Organisms
Heterozygous for a single trait, exhibiting one dominant and one recessive allele, resulting in varied offspring phenotypes upon self-fertilization.
Trait
A characteristic or feature of an organism, determined by genes, that can be inherited and varies among individuals.
Gene
A unit of heredity composed of DNA that determines specific traits by coding for proteins or functional RNA molecules.
Homozygous Dominant
An organism with two identical dominant alleles for a specific trait, resulting in the dominant phenotype.
Alleles Variants
of a gene that arise by mutation and are found at the same place on a chromosome, influencing specific traits.
Gametes
Haploid cells involved in sexual reproduction, carrying half the genetic information of an organism, which combine during fertilization to form a diploid zygote.
Punnett Square
A grid used to predict the genotypes of offspring from a genetic cross, showing how alleles from each parent combine.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, consisting of the specific alleles inherited from its parents, which determines its potential traits.
Homozygous Recessive
An organism with two identical recessive alleles for a specific trait, resulting in the expression of the recessive phenotype.
Cross Fertilization
The fusion of gametes from two different parent organisms, transferring pollen from the male organ of one plant to the female organ of another.
Pollen
Male gametophyte containing sperm cells, essential for fertilizing ovules in plants, enabling sexual reproduction and genetic diversity.
Male Organ
The reproductive structure in male plants that produces and releases pollen for fertilization.
Female Organ
The reproductive structure in plants where ovules are produced and fertilization occurs, typically involving the stigma, style, and ovary.
Filial Generation
The offspring resulting from a cross of the parental generation, denoted as F1, and subsequent generations (F2, F3, etc.).
Parental Generation
The initial set of organisms used in a genetic cross, whose offspring are studied to understand inheritance patterns.
F1 Generation
The initial offspring resulting from a cross between two distinct parental lines, exhibiting a mix of parental traits.
F2 Generation
The generation resulting from the self-fertilization or cross-fertilization of the F1 generation, exhibiting a 3:1 phenotypic ratio in Mendelian inheritance.