Light Reactions of Photosynthesis quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (19)
What is the primary function of the light reactions of photosynthesis?
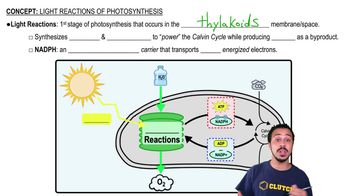
The primary function is to convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
Which molecule is produced by photosystem I during the light reactions?
Photosystem I produces NADPH by reducing NADP+.
What is the role of photosystem II in the light reactions?
Photosystem II functions to oxidize water, releasing oxygen gas and providing electrons to the electron transport chain.
What is the correct order of the steps in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
The correct order is photosystem II, electron transport chain, photosystem I, NADP+ reduction, and chemiosmosis.
Which molecule is oxidized by photosystem II to provide electrons?
Water (H2O) is oxidized by photosystem II, releasing oxygen gas and electrons.
What is the main product of the Calvin cycle that is used to make glucose?
The main product is G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate), which is used to synthesize glucose.
How does photosystem I contribute to the production of NADPH?
Photosystem I excites electrons using light energy and transfers them to NADP+ to form NADPH.
What is the role of ATP synthase in the light reactions?
ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate during chemiosmosis.
What happens to the electrons after they are excited by photosystem II?
The excited electrons are transferred to the electron transport chain.
What is the significance of the electron transport chain in the light reactions?
The electron transport chain helps generate a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Which molecule acts as the final electron acceptor in the light reactions?
NADP+ acts as the final electron acceptor, forming NADPH.
What is the source of the oxygen gas produced during the light reactions?
Oxygen gas is produced from the splitting of water molecules by photosystem II.
What is the role of light energy in the light reactions of photosynthesis?
Light energy is used to excite electrons in photosystems I and II.
How is the proton gradient used to produce ATP in the light reactions?
The proton gradient drives protons through ATP synthase, which synthesizes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
What is the relationship between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle?
The light reactions produce ATP and NADPH, which are used as energy sources in the Calvin cycle to synthesize glucose.
- _____ splits water into 1/2 o2, h+, and e- .Photosystem II splits water into 1/2 O2, H+, and e- during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
- what happens when light energy excites electrons in photosystem ii?When light energy excites electrons in Photosystem II, the electrons are energized and transferred through the electron transport chain, creating a hydrogen ion gradient used to produce ATP.
- which of the following is(are) produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis?The light reactions of photosynthesis produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen (O2) as a byproduct.
- which specific process in the light-dependent reactions produces oxygen and hydrogen ions?The specific process that produces oxygen and hydrogen ions in the light-dependent reactions is the splitting of water molecules by Photosystem II.