Life History exam Flashcards
 Back
BackLife History exam
1/28
Terms in this set (28)
- Life HistoryThe strategic allocation of limited energy, resources, and time impacting traits like survivorship, fecundity, and growth.
- SurvivorshipThe proportion of individuals in a population surviving to a given age.
- FecundityThe capacity or ability for organisms to reproduce, often expressed as the average number of viable offspring produced per reproductive event or lifetime.
- What is a key trade-off in life history?The trade-off between high survivorship and low fecundity.
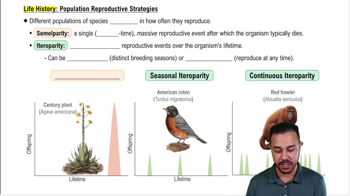
- SemelparityA reproductive strategy involving one massive reproductive event, after which the organism typically dies.
- IteroparityA reproductive strategy involving multiple reproductive events throughout an organism's lifetime.
- What is an example of an organism with high fecundity and low survivorship?Fruit flies, which can produce between 400-900 offspring but have a short lifespan.
- What is an example of an organism with high survivorship and low fecundity?African bush elephants, which produce about 4-6 offspring but have a long lifespan.
- What does the term 'semel' in semelparity mean?Once.
- What does the term 'parity' in semelparity mean?To produce.
- What does the term 'itero' in iteroparity mean?To repeat.
- What is seasonal iteroparity?Reproductive events that occur only during distinct breeding seasons.
- What is continuous iteroparity?Reproductive events that can occur at any time once the organism becomes reproductively capable.
- What is an example of an organism with semelparity?The century plant, which has one massive reproductive event and then dies.
- What is an example of an organism with seasonal iteroparity?The American Robin, which reproduces during distinct breeding seasons.
- What is an example of an organism with continuous iteroparity?The red howler monkey, which can reproduce at any time once reproductively capable.
- What is the relationship between high survivorship and lifespan?High survivorship is often, but not always, associated with having longer lifespans.
- What is the relationship between low survivorship and lifespan?Low survivorship is often, but not always, correlated with having a shorter lifespan.
- What does life history encompass?Any individual trait, strategy, or trade-off impacting an organism's survivorship, fecundity, or developmental growth.
- What is the opposite of survivorship?Mortality, which is the proportion of individuals dying at a given age.
- What is the lifespan of a fruit fly?About a month.
- What is the lifespan of an African bush elephant?About 70 years.
- What does the graph of fecundity vs. survivorship show?A trade-off where most organisms fall on a trend line between high fecundity and low survivorship or vice versa.
- What is a fitness trade-off?A compromise between two traits that cannot be optimized simultaneously, such as between survivorship and fecundity.
- What is the main focus of life history studies?Traits like survivorship, fecundity, and growth.
- What is the reproductive capacity of a single female fruit fly?Between 400-900 offspring.
- How many offspring do African bush elephants typically produce?About 4-6 offspring throughout their entire lifespans.
- What is the significance of the term 'life history'?It can be thought of as the organism's entire life story, encompassing all traits and strategies impacting its survival and reproduction.