Back
BackIonic Bonding definitions
Terms in this set (9)
Charge
The net electrical property of an atom or molecule, determined by the difference between the number of protons (positive) and electrons (negative).
Positive
A state where an atom has more protons than electrons, resulting in a net positive charge.
Negative
An atom or molecule with more electrons than protons, resulting in a net negative charge.
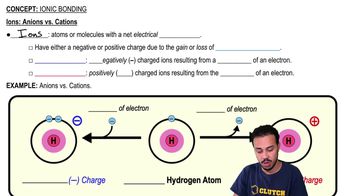
Anion
A negatively charged ion formed when an atom gains one or more electrons, resulting in more electrons than protons.
Cation
A positively charged ion formed when an atom loses one or more electrons, resulting in more protons than electrons.
Ion
An atom or molecule with a net electric charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
First Shell
The innermost electron shell of an atom, which can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, determining the atom's initial electron configuration and stability.
Second Shell
The second electron shell can hold up to 8 electrons and is the next energy level after the first shell, playing a crucial role in an atom's chemical reactivity and bonding.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom that determine its chemical reactivity and bonding behavior.