Introduction to Water exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
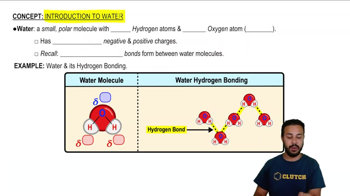
Water molecule
A small polar molecule with the chemical formula H2O.
What is the chemical formula of water?
H2O
Polar covalent bonds
Bonds where electrons are shared unequally, leading to partial charges on atoms.
What type of bond allows water to have partial charges?
Polar covalent bonds
Partial negative charge in water
Located on the oxygen atom within a water molecule.
Where is the partial positive charge in a water molecule?
On the hydrogen atoms.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds that form between the partial positive charge of hydrogen in one water molecule and the partial negative charge of oxygen in another.
What allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds?
The partial negative and partial positive charges on different atoms.
Cohesion
The property of water that allows it to stick to itself due to hydrogen bonding.
What is adhesion?
The property of water that allows it to stick to other substances.
Surface tension
The elastic tendency of water's surface, caused by hydrogen bonding.
Why does ice have a low density compared to liquid water?
Because the hydrogen bonds in ice form a lattice structure that is less dense.
High specific heat
The property of water that allows it to absorb a lot of heat without a significant increase in temperature.
What is the significance of water's high specific heat?
It helps regulate temperature in the environment and within organisms.
Universal solvent
A term used to describe water's ability to dissolve many different substances.
Why is water called a universal solvent?
Because it can dissolve a wide variety of substances due to its polarity.
Emergent properties of water
Properties that arise from hydrogen bonding, including cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, low density of ice, high specific heat, and being a universal solvent.
What are the four emergent properties of water?
Cohesion/adhesion/surface tension, low density of ice, high specific heat, and being a universal solvent.
Role of water in biological processes
Water's properties influence cellular functions and climate regulation.
How does water support life on Earth?
Through its unique properties like cohesion, adhesion, surface tension, low density of ice, high specific heat, and being a universal solvent.
Hydrogen bonding in water
Occurs between the hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another.
What is the effect of hydrogen bonding on water's properties?
It gives rise to water's emergent properties that are essential for life.
Polarity of water
Water has a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and partial positive charges on the hydrogen atoms.
What is the significance of water's polarity?
It allows water to form hydrogen bonds and interact with various substances.
Heat of vaporization
The amount of energy required to convert water from liquid to gas.
Why is water's heat of vaporization important?
It helps in cooling mechanisms like sweating and transpiration.
Density of ice
Ice is less dense than liquid water due to the lattice structure formed by hydrogen bonds.
What property of water allows ice to float?
Its low density in the solid form.
Climate regulation
Water's high specific heat helps stabilize Earth's climate by absorbing and releasing heat.