Introduction to Water definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (8)
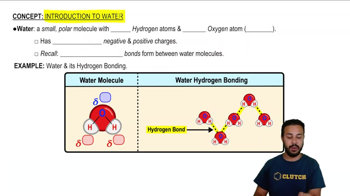
Water
A small polar molecule with the formula H₂O, featuring partial charges that enable hydrogen bonding, crucial for its unique properties like cohesion, high heat capacity, and solvent abilities.
Polar Covalent Bonds
A type of chemical bond where electrons are shared unequally between atoms, resulting in partial positive and negative charges on different parts of the molecule.
Hydrogen Bonds
Attractive forces between the partial positive charge of hydrogen in one molecule and the partial negative charge of oxygen in another, crucial for water's unique properties.
Cohesion
The attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding, enabling them to stick together, which is crucial for processes like water transport in plants.
High Heat Capacity
The ability of water to absorb and retain large amounts of heat with minimal temperature change, due to hydrogen bonding between molecules.
Solvent
A substance that dissolves other substances due to its polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds, facilitating chemical reactions and transport in biological systems.
Polarity
The distribution of electrical charge across a molecule, leading to regions of partial positive and negative charges, enabling interactions like hydrogen bonding.
Emergent Properties
Complex characteristics arising from the interaction of simpler elements, such as water's cohesion and high heat capacity, due to its polarity and hydrogen bonding.