Introduction to Mendel's Experiments definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (13)
Gregor Mendel
Pioneering scientist who established the foundational principles of genetics through his methodical experiments with pea plants, identifying how traits are inherited.
Genetics
the study of how traits are inherited through the interactions of alleles, focusing on the transmission of genetic information from parents to offspring.
Pea Plants
A model organism used by Gregor Mendel to study inheritance, characterized by easily distinguishable traits, rapid development, and the ability to produce many offspring.
Model Organism
Non-human species extensively studied to understand biological processes applicable to other organisms, including humans, due to their ease of manipulation, rapid development, and observable traits.
Character
An inherited feature that varies among individuals, such as plant height or flower color, used to study genetic differences.
Trait
A specific variant of an inherited feature, such as tall or short plant height, or purple or white flower color, within an organism.
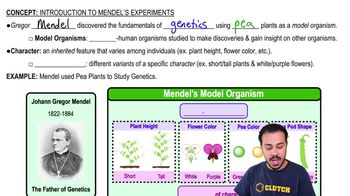
Flower Color
An inherited feature in pea plants that varies among individuals, with traits such as white or purple, used by Mendel to study genetic variation.
Pea Color
The genetic character in pea plants that varies between green and yellow, used by Mendel to study inheritance patterns.
Pea Pod Shape
The shape of the pea pod, a character in Mendel's experiments, can exhibit traits such as being either straight or bumpy.
Heredity
The transmission of genetic characteristics from parents to offspring, determining traits such as height and color, as studied by Mendel using pea plants.
Offspring
The result of reproduction, inheriting genetic material from one or more parents, leading to a new individual organism.
Parent
An organism that contributes genetic material to its offspring through reproduction, influencing inherited traits and characteristics.
Pisum Sativum
Model organism used by Gregor Mendel to study inheritance, known for its easily distinguishable traits, rapid growth, and high offspring yield.