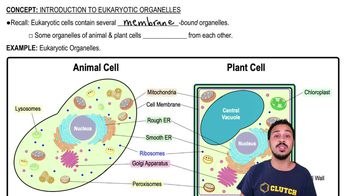
Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Eukaryotic Organelles quiz
1/31
Terms in this set (31)
- What is the primary function of ribosomes in a eukaryotic cell?Ribosomes are molecular machines that build proteins through a process called translation.
- Are ribosomes considered membranous or non-membranous organelles?Ribosomes are considered non-membranous organelles.
- Where can ribosomes be found within a eukaryotic cell?Ribosomes can be found free-floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- What is the process called that ribosomes use to build proteins?The process is called translation.
- What distinguishes free ribosomes from attached ribosomes?Free ribosomes float in the cytoplasm, while attached ribosomes are bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
- What is the cytoplasm in a eukaryotic cell?The cytoplasm is the area inside the cell but outside the organelles.
- What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER) known for?The rough ER is known for having ribosomes attached to its surface and being involved in protein secretion.
- What are vesicles in the context of the endomembrane system?Vesicles are tiny membrane bubbles that carry materials between organelles.
- Which organelles are part of the endomembrane system involved in protein secretion?The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and transport vesicles are involved in protein secretion.
- What are the two main functions of the endomembrane system discussed in the lesson?The two main functions are protein secretion and cellular digestion.
- What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in the endomembrane system?The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion.
- What is the significance of the nuclear envelope in eukaryotic cells?The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus and is part of the endomembrane system involved in protein secretion.
- What are lysosomes and peroxisomes primarily involved in?Lysosomes and peroxisomes are primarily involved in cellular digestion.
- What is the function of the central vacuole in plant cells?The central vacuole stores nutrients and waste products and helps maintain turgor pressure in plant cells.
- What is the primary function of the mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?Mitochondria are involved in energy production through aerobic respiration.
- nucleoli are present during _____.Nucleoli are present during interphase.
- what evolutionary advantage does compartmentalization of core metabolic processes offer eukaryotes?Compartmentalization allows for increased efficiency and specialization of metabolic processes, reducing interference between different biochemical pathways and enabling more complex regulation.
- which of the following pairs of pathways and their location in the cell is incorrectly matched?Without the specific pairs provided, it's difficult to determine the incorrect match. However, an example of an incorrect match would be glycolysis occurring in the mitochondria, as it actually occurs in the cytoplasm.
- which statement correctly describes the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell?The nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell consists of a double membrane that encloses the nucleus, separating it from the cytoplasm, and contains nuclear pores for transport of molecules.
- which organelles are labeled g? centrioles lysosomes ribosomes mitochondriaWithout the specific diagram, it's not possible to determine which organelles are labeled 'g'. However, common organelles include centrioles, lysosomes, ribosomes, and mitochondria.
- which of these processes takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell?Processes such as glycolysis and translation by free ribosomes take place in the cytoplasm of a cell.
- which of these is true of the cytoplasm of an unfertilized egg?The cytoplasm of an unfertilized egg contains nutrients, organelles, and molecular machinery necessary for early development post-fertilization.
- the functions of the rough endoplasmic reticulum include which of the following?The rough endoplasmic reticulum is involved in the synthesis of proteins destined for secretion, membrane insertion, or lysosomes, and it is studded with ribosomes.
- which organelle is a fine network of tubular structures?The endoplasmic reticulum, particularly the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, is a fine network of tubular structures.
- can you label the structures of a plant cell?Yes, key structures of a plant cell include the cell wall, chloroplasts, central vacuole, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and ribosomes.
- what is the function of the connector proteins?Connector proteins, such as those in cell junctions, help to link cells together, providing structural support and facilitating communication between cells.
- which organelle is labeled g? cytoplasm cell wall cell membrane vacuoleWithout the specific diagram, it's not possible to determine which organelle is labeled 'g'. However, common organelles include the cytoplasm, cell wall, cell membrane, and vacuole.
- what is the function of the small, dark organelles labeled e?Without the specific diagram, it's not possible to determine the function of the organelles labeled 'e'. However, small, dark organelles could be ribosomes, which are involved in protein synthesis.
- in the figure below, working from the inside out, what would be the order of components observed?Without the specific figure, it's not possible to determine the exact order. However, a common sequence might be the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and cell wall (in plant cells).
- which organelles are not found in plant cells?Lysosomes and centrioles are organelles typically not found in plant cells.
- which of the following processes takes place in the cytoplasm?Glycolysis and translation by free ribosomes are processes that take place in the cytoplasm.