Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (29)
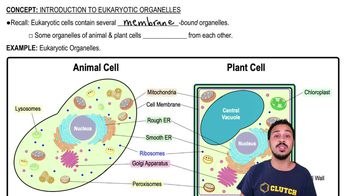
What are Eukaryotic cells?
Cells that contain membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus.
What are lysosomes?
Organelles found only in animal cells that contain digestive enzymes.
Define Chloroplasts
Organelles found only in plant cells that conduct photosynthesis.
What is the function of ribosomes?
To build proteins through the process of translation.
What is endomembrane system?
A group of organelles involved in protein and lipid synthesis, including the ER and Golgi apparatus.
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER)?
An organelle with ribosomes attached, involved in protein synthesis.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (smooth ER)
An organelle involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
What are peroxisomes?
Organelles that contain enzymes to break down fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances.
Define Golgi apparatus.
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
What is the function of mitochondria?
To generate ATP through cellular respiration, providing energy for the cell.
What is Cell wall?
A rigid layer found outside the cell membrane in plant cells, providing structural support and protection.
What is the cytoskeleton?
A network of protein filaments that provide structural support and facilitate cell movement.
Microfilaments
Thin protein fibers that play a role in cell movement and shape.
What are microtubules?
Hollow tubes that help maintain cell shape and are involved in intracellular transport and cell division.
Intermediate filaments
Protein fibers that provide mechanical support for the cell.
What are tight junctions?
Cell junctions that create a watertight seal between adjacent cells.
Anchoring junctions
Cell junctions that attach cells to each other or to the extracellular matrix.
What are gap junctions?
Channels that allow for direct communication between adjacent cells.
Plasmodesmata
Channels between plant cells that allow for transport and communication.
What is the role of the nucleus?
To store genetic information and control cellular activities.
What are Vacuoles?
Storage organelles in cells, larger in plant cells, used for storing nutrients, waste products, and maintaining turgor pressure.
What is translation?
The process by which ribosomes build proteins from mRNA.
Free ribosomes
Ribosomes that are free-floating in the cytoplasm and synthesize proteins that function within the cytoplasm.
Attached ribosomes
Ribosomes attached to the rough ER, synthesizing proteins destined for secretion or for use in lysosomes.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
To regulate the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Protein secretion
The process by which proteins are synthesized, modified, and transported out of the cell.
What are energy-related organelles?
Organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts involved in energy production and conversion.
Cellular digestion
The process involving lysosomes and peroxisomes to break down macromolecules and detoxify substances.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus?
To modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.