Introduction to Eukaryotic Organelles definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (16)
Eukaryotic Organelles
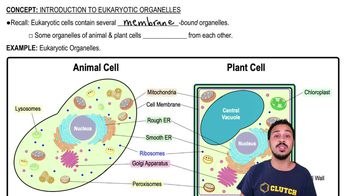
Membrane-bound structures within eukaryotic cells, each with specific functions, found in both plant and animal cells, though some are unique to each type.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, found in both animals and plants, but with some organelles unique to each type.
Membrane Bound Organelles
Organelles enclosed by lipid bilayers, found in eukaryotic cells, performing specialized functions such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste processing.
Animal Cells
Eukaryotic cells unique to animals, containing membrane-bound organelles like lysosomes, but lacking chloroplasts and cell walls found in plant cells.
Plant Cells
Cells with a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and large central vacuoles, distinct from animal cells.
Lysosomes
Organelles in animal cells containing enzymes that digest cellular waste, pathogens, and damaged organelles, maintaining cellular health.
Chloroplasts
Organelles in plant cells that convert light energy into chemical energy via photosynthesis, containing the pigment chlorophyll.
Cell Walls
Rigid outer layer found in plant cells, providing structural support and protection, composed mainly of cellulose.
Mitochondria
Organelles in eukaryotic cells that generate ATP through cellular respiration, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
A membrane-bound organelle studded with ribosomes, crucial for synthesizing and folding proteins destined for secretion or membrane integration.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
A membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells that synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbohydrates, detoxifies drugs and poisons, and stores calcium ions.
Ribosomes
Cellular structures found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that synthesize proteins by translating messenger RNA (mRNA).
Golgi Apparatus
An organelle in eukaryotic cells that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Peroxisomes
Organelles in eukaryotic cells that detoxify harmful substances and break down fatty acids using oxidative enzymes.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, with DNA in a nucleoid region, typically found in bacteria and archaea.
Proteins
Chains of amino acids folded into specific shapes, essential for cell structure, function, and regulation, synthesized by ribosomes in all cell types.