Introduction to DNA Cloning exam Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to DNA Cloning exam
1/28
Terms in this set (28)
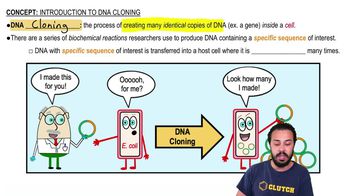
- DNA CloningThe process of creating multiple identical copies of a specific DNA sequence.
- What is the role of E. coli in DNA cloning?E. coli serves as a host cell for replicating the inserted DNA sequence.
- Recombinant DNAA molecule containing DNA from two different sources.
- What are bacterial plasmids?Small, circular DNA molecules that replicate independently from the bacterial genome.
- Cloning VectorsMolecules such as plasmids that carry foreign DNA into a host cell for replication.
- What is the purpose of cloning vectors?To carry a gene of interest into a host cell for replication.
- Biochemical Reactions in DNA CloningProcesses used to produce DNA containing a specific sequence of interest.
- What is the significance of recombinant DNA in genetic experiments?It allows for the combination of DNA from different species, facilitating genetic studies and engineering.
- Host CellA cell into which DNA is inserted for replication.
- What is the function of a host cell in DNA cloning?To replicate the inserted DNA sequence through its normal replication process.
- Gene of InterestA specific DNA sequence that researchers aim to clone.
- What is a recombinant DNA molecule?A single molecule that has DNA from two different sources.
- ReplicationThe process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA.
- What are the two sources of DNA in recombinant DNA?Often from different species, such as bacteria and humans.
- Bacterial PlasmidA small, circular DNA molecule found in bacteria used as a cloning vector.
- What is the role of bacterial plasmids in DNA cloning?They serve as cloning vectors to carry foreign DNA into host cells.
- Foreign DNADNA that originates from a different organism or species.
- What happens to the foreign DNA once it is inside the host cell?It is replicated by the host cell during its normal replication process.
- Genetic EngineeringThe manipulation of an organism's genes using biotechnology.
- What is the importance of understanding DNA cloning?It is essential for advancements in genetic engineering and biotechnology.
- Replication of Recombinant DNAOccurs when the host cell replicates, producing copies of the recombinant DNA.
- What is the outcome of DNA cloning?Multiple identical copies of the specific DNA sequence of interest.
- BiotechnologyThe use of living systems and organisms to develop or make products.
- What is the first step in DNA cloning?Producing DNA containing a specific sequence of interest through biochemical reactions.
- Cloning with Recombinant DNAUsing recombinant DNA molecules as cloning vectors to carry genes of interest into host cells.
- What is the significance of bacterial plasmids in cloning?They are used as vectors to introduce foreign DNA into host cells for replication.
- Host Cell ReplicationThe process by which a host cell duplicates its DNA, including any inserted foreign DNA.
- What is the role of a scientist in DNA cloning?To create the specific DNA molecule with the sequence of interest and insert it into a host cell.