Introduction to DNA Cloning definitions Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (18)
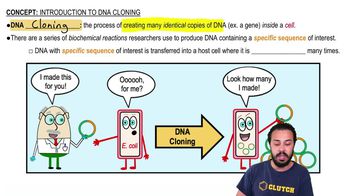
DNA Cloning
The process of creating multiple identical copies of a specific DNA sequence by inserting it into a host cell, which then replicates the DNA through its normal cellular processes.
Gene
A segment of DNA that contains the instructions for building a specific protein or set of proteins, influencing traits and functions within an organism.
Bacterial Cell
A unicellular organism lacking a nucleus, with DNA in a single circular chromosome, often used in genetic research and cloning due to its rapid replication.
E. Coli
A common bacterium used in DNA cloning to replicate specific DNA sequences, facilitating the production of multiple identical copies of the DNA of interest.
Biochemical Reactions
Chemical processes in living organisms that convert substrates into products, often involving enzymes, to sustain life and cellular functions.
Host Cell
A cell that receives foreign DNA for replication and cloning, often used in genetic engineering to produce multiple copies of a specific DNA sequence.
Sequence
A specific order of nucleotides in a DNA or RNA molecule that encodes genetic information.
Recombinant DNA
DNA composed of sequences from two different sources, often from different species, combined to create new genetic combinations.
DNA Technology
The manipulation and combination of DNA from different sources to create recombinant DNA for research medicine, or agriculture.
Human Gene
A segment of DNA in humans that encodes instructions for building proteins or functional RNA molecules, influencing traits and biological functions.
Plant Gene
A gene in plants that encodes specific traits, functions, or responses, and can be cloned or combined with genes from other species to create recombinant DNA.
Restriction Enzyme
A protein that cuts DNA at specific sequences, creating fragments useful for genetic engineering and molecular cloning.
Target DNA
DNA sequence of interest to be cloned or analyzed, often inserted into a host organism for replication.
DNA Ligase
An enzyme that facilitates the joining of DNA strands by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bond, essential in DNA replication and repair.
Enzyme
A protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions, speeding up the process without being consumed or altered in the reaction.
Bacterial Chromosome
A single, circular DNA molecule in bacteria containing essential genes for survival and replication, distinct from plasmids, and not enclosed in a nucleus.
Plasmid
A small, circular DNA molecule found in bacteria, separate from chromosomal DNA, often used in genetic engineering to replicate specific DNA sequences.
Species
A group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, sharing common characteristics and genetic makeup, and distinct from other groups in terms of reproduction and genetics.