Introduction to Community Ecology exam Flashcards
 Back
BackIntroduction to Community Ecology exam
1/28
Terms in this set (28)
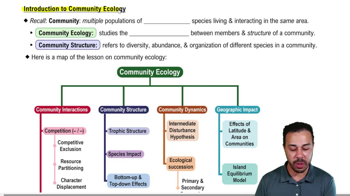
- Community EcologyThe study of interactions among various species within a community, focusing on structure, diversity, and abundance.
- CommunityMultiple populations of different species living and interacting in the same area.
- Community StructureRefers to the diversity, abundance, and overall organization of different species in a community.
- What are the four main types of community interactions?Competition, exploitation, mutualism, and commensalism.
- CompetitionAn interaction where species vie for the same resources in an ecosystem.
- ExploitationAn interaction where one species benefits at the expense of another, including predation, herbivory, and parasitism.
- MutualismAn interaction where both species benefit from the relationship.
- CommensalismAn interaction where one species benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed.
- What is competitive exclusion?The principle that two species competing for the same resources cannot coexist if other ecological factors are constant.
- Resource PartitioningThe division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche.
- Character DisplacementThe phenomenon where differences among similar species are accentuated in regions where the species co-occur.
- PredationAn interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, the prey.
- HerbivoryAn interaction where an organism eats parts of a plant or alga.
- ParasitismAn interaction where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in another organism, the host, causing it harm.
- Trophic StructureThe feeding relationships between organisms in a community.
- What are bottom-up and top-down effects?Bottom-up effects are driven by the presence or absence of producers, while top-down effects are driven by the presence or absence of top predators.
- Ecological SuccessionThe process of change in the species structure of an ecological community over time.
- Primary SuccessionSuccession that occurs in an area where no previous community existed.
- Secondary SuccessionSuccession that occurs in areas where a community previously existed but was disturbed.
- Intermediate Disturbance HypothesisThe concept that moderate levels of disturbance can foster greater species diversity than low or high levels of disturbance.
- Geographic ImpactThe influence of geographic factors like latitude and area on community composition.
- Latitude EffectThe observation that species diversity tends to be higher near the equator and lower towards the poles.
- Area EffectThe principle that larger areas tend to have more species than smaller areas.
- Island Equilibrium ModelA model that describes the balance between immigration and extinction rates on islands.
- What is the significance of biodiversity in ecosystem stability?Biodiversity enhances ecosystem stability by providing a variety of species that can adapt to changes and disturbances.
- Species InteractionsThe various ways in which species interact within a community, including competition, exploitation, mutualism, and commensalism.
- What does community ecology focus on?It focuses on the interactions among species, community structure, diversity, abundance, and the effects of geographic factors.
- Species ImpactThe influence that a species has on the structure and function of a community.