Introduction to Cellular Respiration quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (42)
What is the main purpose of aerobic cellular respiration?
The main purpose of aerobic cellular respiration is to produce lots of ATP or energy for the cell.
What does the term 'aerobic' imply in the context of cellular respiration?
The term 'aerobic' implies that the process requires the presence of oxygen gas (O2).
Where do most stages of aerobic cellular respiration occur within the cell?
Most stages of aerobic cellular respiration occur inside the mitochondria of the cell.
What are the end products of aerobic cellular respiration?
The end products of aerobic cellular respiration are carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O), and ATP.
What is the chemical formula for glucose, the primary substrate in cellular respiration?
The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6.
What is the role of oxygen in aerobic cellular respiration?
Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, allowing the production of water.
What mnemonic can help you remember the stages of aerobic cellular respiration in order?
The mnemonic 'Giant Pandas Killed Elvis' helps remember the stages: Glycolysis, Pyruvate oxidation, Krebs cycle, and Electron transport chain.
Which stage of aerobic cellular respiration occurs in the cytoplasm?
Glycolysis is the stage that occurs in the cytoplasm.
What happens to glucose during aerobic cellular respiration?
Glucose is oxidized, losing electrons and being converted into carbon dioxide.
What is the significance of ATP in cellular respiration?
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) is the primary energy currency of the cell, produced during cellular respiration.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not.
What is the Krebs cycle also known as?
The Krebs cycle is also known as the citric acid cycle.
What are the byproducts of aerobic cellular respiration besides ATP?
The byproducts are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
What is the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
The electron transport chain generates a proton gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP.
What is the first stage of aerobic cellular respiration?
The first stage is Glycolysis.
- what do alcohol fermentation, acetyl coa formation, and the krebs cycle have in common?All three processes are involved in cellular respiration and energy production, but they differ in their oxygen requirements and pathways. Alcohol fermentation is anaerobic, while acetyl CoA formation and the Krebs cycle are aerobic processes.
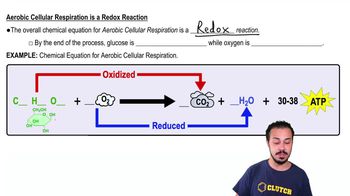
- what is the correct equation for cellular respiration?The correct equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP.
- what is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are complementary processes. Photosynthesis converts carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, while cellular respiration converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy as ATP.
- which statement describes the reaction for cellular respiration?Cellular respiration is a redox reaction where glucose is oxidized and oxygen is reduced, resulting in the production of ATP, carbon dioxide, and water.
- which actions could be categorized in the “aerobic” section of the venn diagram?Actions such as the Krebs cycle, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation are categorized as aerobic because they require oxygen.
- what process is the source of the co2 that root hairs release into the soil?The source of CO2 released by root hairs is cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down to produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
- in which organelle does cellular respiration take place?Cellular respiration primarily takes place in the mitochondria.
- in which way are photosynthesis and cellular respiration different?Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts and converts light energy into chemical energy, while cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria and converts chemical energy in glucose into ATP.
- in what organelle does cellular respiration take place?Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria.
- what role does cellular respiration play in the carbon cycle?Cellular respiration releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, which is then used by plants in photosynthesis, thus playing a crucial role in the carbon cycle.
- in what cell organelle does cellular respiration occur?Cellular respiration occurs in the mitochondria.
- which is the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are interconnected; the products of photosynthesis (glucose and oxygen) are the reactants for cellular respiration, and vice versa.
- how are cellular respiration and photosynthesis related, in terms of energy?Photosynthesis stores energy in glucose molecules, while cellular respiration releases energy from glucose to form ATP.
- the electrons stripped from glucose in cellular respiration ultimately end up in which compound?The electrons stripped from glucose ultimately end up in water, as oxygen is reduced to form water.
- which molecule is a direct product of this cellular process?ATP is a direct product of cellular respiration.
- which is required for both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration?Both anaerobic and aerobic respiration require glucose as a starting substrate.
- which word equation best represents the process of cellular respiration?The word equation for cellular respiration is: Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP).
- which statement best compares aerobic and anaerobic respiration?Aerobic respiration requires oxygen and produces more ATP, while anaerobic respiration does not require oxygen and produces less ATP.
- for each glucose that enters glycolysis, _____ acetyl coa enter the citric acid cycle.For each glucose that enters glycolysis, 2 acetyl CoA molecules enter the citric acid cycle.
- what is the chemical equation for cellular respiration?The chemical equation for cellular respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP.
- molecular oxygen (o2) has what role in aerobic cellular respiration?Molecular oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, forming water.
- why is formation of atp by atp synthase in the mitochondria known as oxidative phosphorylation?It is called oxidative phosphorylation because it involves the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain to oxygen, driving ATP synthesis.
- in which organelles does cellular respiration take place?Cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria.
- what would happen to a cell if cellular respiration suddenly ceased?If cellular respiration ceased, the cell would be unable to produce ATP, leading to energy depletion and eventual cell death.
- what is the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?Photosynthesis and respiration are complementary processes; photosynthesis converts CO2 and water into glucose and oxygen, while respiration converts glucose and oxygen back into CO2 and water.
- which cell type(s) had the highest rate of oxygen consumption?Cells with high metabolic activity, such as muscle cells, typically have the highest rate of oxygen consumption.
- what are the three stages of cellular respiration?The three main stages of cellular respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain.