Introduction to Cellular Respiration definitions Flashcards
Terms in this set (12)
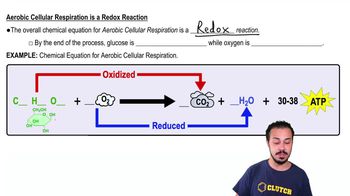
Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The process of converting glucose and oxygen into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water, primarily occurring in the mitochondria and requiring oxygen.
ATP
The primary energy carrier in cells, produced during cellular respiration, essential for powering cellular processes.
Glucose
A monosaccharide that serves as a primary energy source in cellular respiration, converting into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water in the presence of oxygen.
Mitochondria
The powerhouse of the cell, where glucose and oxygen are converted into ATP, carbon dioxide, and water through aerobic cellular respiration.
Oxygen Gas
A diatomic molecule essential for aerobic respiration, serving as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain, enabling ATP production in cells.
Carbon Dioxide
A byproduct of aerobic cellular respiration, this gas is produced when glucose is oxidized and is expelled from the body through exhalation.
Water
A polar molecule essential for life, acting as a solvent, temperature buffer, and reactant/product in biochemical reactions, including cellular respiration.
Pyruvate Oxidation
The conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, producing NADH and CO₂, and linking glycolysis to the Krebs cycle in aerobic respiration.
Krebs Cycle
A key stage in aerobic respiration where acetyl-CoA is oxidized, producing NADH, FADH2, and ATP, and releasing CO2 in the mitochondrial matrix.
Citric Acid Cycle
A key metabolic pathway in aerobic respiration that generates ATP, NADH, and FADH2 by oxidizing acetyl-CoA, producing CO2 as a byproduct, and occurs in the mitochondria.
Electron Transport Chain
A series of protein complexes in the mitochondria that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions, creating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis.
Chemiosmosis
The process where ATP is generated as protons move down their gradient through ATP synthase in the mitochondrial membrane.