Innate Immunity exam Flashcards
 Back
BackInnate Immunity exam
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
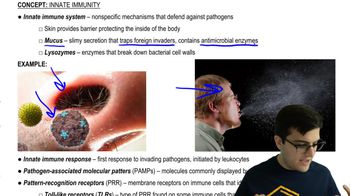
- Innate Immune SystemThe body's first line of defense against pathogens, employing a nonspecific response.
- What is the role of the skin in the innate immune system?Acts as a physical barrier to protect the body from pathogens.
- MucusA slimy secretion that traps foreign invaders and contains antimicrobial enzymes.
- What are leukocytes?White blood cells that initiate the innate immune response.
- PhagocytosisThe process by which phagocytes engulf and digest pathogens.
- Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs)Membrane receptors that identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
- What do Toll-like receptors (TLRs) do?They identify PAMPs and initiate a signaling cascade to recruit other immune cells.
- Inflammatory ResponseA response characterized by swelling and recruitment of immune cells to combat infections.
- Complement SystemA system of proteins that aids in lysing pathogens and enhancing immune defense.
- What is the function of neutrophils?Phagocytes that circulate in the blood and are attracted to infected tissues by cytokines.
- MacrophagesPhagocytes that reside in tissues and organs, defending against pathogens.
- What is the role of dendritic cells?Phagocytes that stimulate the adaptive immune system by presenting antigens.
- EosinophilsImmune cells that defend against multicellular parasites.
- Natural Killer CellsCells that identify and destroy virus-infected cells by triggering apoptosis.
- What are interferons?Cytokines that induce cells to interfere with viral replication.
- ChemokinesA type of cytokine that recruits cells to the infection site.
- What do mast cells release?Histamine, which constricts blood vessels to reduce blood flow and prevent blood loss.
- CytokinesSignaling molecules that attract other immune cells and help mount an immune response.
- What is the role of lysozymes?Enzymes that break down bacterial cell walls.
- Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs)Molecules commonly displayed by pathogens that are recognized by the immune system.
- What is the function of TLR4?Recognizes lipopolysaccharides from bacteria and releases cytokines in response.
- HistamineA chemical signal released by mast cells that constricts blood vessels in the area of infection.
- What is the role of the complement proteins?Form pores in the membranes of pathogens, causing them to lyse.
- NeutrophilsPhagocytes that circulate in the blood and are attracted to infected tissues by cytokines.
- What is the purpose of the inflammatory response?To recruit immune cells to the site of infection and combat pathogens.
- Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)A type of PAMP found on the surface of bacterial cells.
- What do chemokines do?Recruit immune cells to the site of infection.
- PhagocytesCells that perform phagocytosis to eliminate pathogens.
- What is the role of cytokines in the immune response?They attract other immune cells and help mount an immune response.