Back
BackGrowth definitions
Terms in this set (13)
Indeterminate Growth
Continuous plant growth throughout life, enabled by meristems, allowing roots and shoots to extend indefinitely.
Meristems
Regions in plants containing undifferentiated cells capable of division and differentiation into various tissues, enabling continuous growth throughout the plant's life.
Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells capable of dividing and developing into various specialized cell types, essential for growth and repair in organisms.
Primary Growth
Growth involving the elongation of roots and shoots, driven by apical meristems, enabling plants to extend deeper into the soil and higher towards light.
Apical Meristem
A region of undifferentiated cells at the tips of roots and shoots, responsible for primary growth by producing new cells that differentiate into various plant tissues.
Root Apical Meristem
A region of undifferentiated cells at the tip of a root, responsible for primary growth by producing new cells that elongate and differentiate into various root tissues.
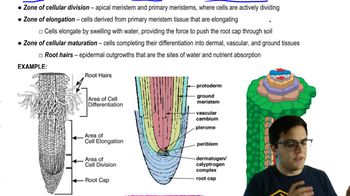
Primary Meristems
Meristems derived from apical meristems, responsible for primary growth, forming protoderm (epidermis), procambium (vascular tissue), and ground meristem (ground tissue).
Protoderm
The outermost primary meristem in plants, responsible for forming the epidermis, the protective outer layer of cells.
Epidermis
The outermost layer of cells in plants, providing protection against environmental factors and aiding in water retention and gas exchange.
Procambium
A primary meristem that differentiates into vascular tissues, including xylem and phloem, and can further develop into vascular cambium and cork cambium for secondary growth.
Vascular Tissue
Plant tissue responsible for transporting water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant, consisting of xylem and phloem, derived from the procambium.
Ground Tissue
Plant tissue excluding vascular and dermal tissues, involved in photosynthesis, storage, and support, found in roots, stems, and leaves, and divided into pith and cortex in shoots.
Root Cap
A protective structure at the tip of a plant root that shields the apical meristem, senses gravity, and secretes lubricating polysaccharides to aid root penetration through soil.