Gas Exchange exam Flashcards
 Back
BackTerms in this set (27)
Gas Exchange
The process by which oxygen enters the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is expelled, primarily occurring in the alveoli of the lungs.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
What factors influence the diffusion of gases?
Surface area, distance, and partial pressure differences.
Hemoglobin
A protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen and exhibits cooperative binding.
What is the oxygen dissociation curve?
A graph that shows the relationship between the partial pressure of oxygen and the saturation of hemoglobin.
Bohr Shift
A rightward shift of the oxygen dissociation curve due to lower pH or higher carbon dioxide levels, facilitating oxygen delivery to tissues.
Diaphragm
A muscle that plays a crucial role in breathing by creating negative pressure in the thoracic cavity.
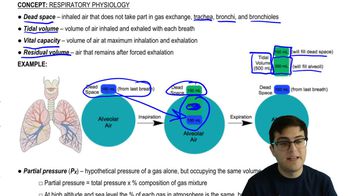
What is tidal volume?
The volume of air inhaled and exhaled during normal breathing.
Dead Space
The portion of the respiratory system where air does not participate in gas exchange, such as the trachea and bronchi.
What is vital capacity?
The maximum volume of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Residual Volume
The volume of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation.
Partial Pressure
The hypothetical pressure of a gas if it alone occupied the volume of the mixture at the same temperature.
What drives the diffusion of gases?
Partial pressure differences.
Fick's Law of Diffusion
Describes the rate of diffusion of gases, influenced by surface area, distance, and partial pressure differences.
What is cooperative binding in hemoglobin?
The property where the binding of one oxygen molecule makes it easier to bind subsequent oxygen molecules.
Positive Pressure Ventilation
A method of breathing where air is pushed into the lungs, as seen in frogs.
Negative Pressure Ventilation
A method of breathing where air is pulled into the lungs by creating negative pressure in the thoracic cavity.
What is the role of the medulla oblongata in gas exchange?
It contains pH detectors that regulate ventilation based on the acidity of the blood.
Carbonic Acid
Formed when carbon dioxide combines with water in the blood, lowering pH and facilitating the Bohr shift.
What happens to the partial pressure of gases at higher altitudes?
The partial pressure of gases decreases, although their composition remains the same.
Citric Acid Cycle
A metabolic pathway that produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which is then expelled during gas exchange.
What is the significance of the sigmoidal shape of the oxygen dissociation curve?
It indicates cooperative binding, where hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen increases as more oxygen binds.
What is the effect of increasing CO2 on hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen?
It lowers hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, facilitating oxygen unloading in tissues.
Surface Area
A factor that increases the rate of gas diffusion; more surface area allows for more efficient gas exchange.
Distance
A factor that affects the rate of gas diffusion; shorter distances increase the rate of diffusion.
What is the role of mitochondria in gas exchange?
Mitochondria use oxygen as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain and produce CO2 as a byproduct.
What is the effect of lower pH on hemoglobin's oxygen affinity?
Lower pH decreases hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, promoting oxygen release to tissues.