Flowers quiz Flashcards
 Back
BackFlowers quiz
1/29
Terms in this set (29)
- What are the male and female reproductive structures of flowers called?The male reproductive structure is called the stamen, and the female reproductive structure is called the carpal.
- What are the two main components of the stamen?The stamen is composed of the filament and the anther.
- What is the function of the anther in a flower?The anther contains the microsporangium, which produces microspores.
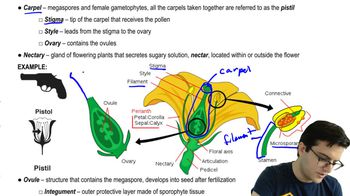
- What is the role of the stigma in the carpal?The stigma is the tip of the carpal where pollen lands and is received during the reproductive process.
- What is the function of the style in a flower's carpal?The style is the pathway that leads from the stigma to the ovary.
- What does the ovary of a flower contain?The ovary contains ovules, which receive sperm from the male portions of flowers.
- What is the purpose of the nectary in flowers?The nectary secretes nectar, a sugary solution that attracts pollinators.
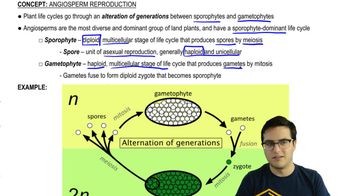
- What is the significance of pollen in plant reproduction?Pollen is the male gametophyte that allows for diverse methods of connecting sperm and egg, and it is surrounded by a watertight coating made of sporopollenin.
- What is double fertilization in angiosperms?Double fertilization involves one sperm fertilizing the egg to form the embryo, and another sperm interacting with polar nuclei to form endosperm.
- What is the difference between monoecious and dioecious plants?Monoecious plants have both male and female flowers on the same plant, while dioecious plants have male and female flowers on separate plants.
- What is self-incompatibility in plants?Self-incompatibility is a genetic mechanism that prevents self-pollination, encouraging outcrossing.
- What are cotyledons in embryonic plants?Cotyledons are embryonic leaves, with monocots having one cotyledon and eudicots having two.
- What is the role of the endosperm in seed development?The endosperm is a nutrient-rich tissue that surrounds the embryo and provides it with starch, protein, and oil.
- What is coevolution in the context of pollination syndromes?Coevolution is when the evolution of one species influences the evolution of another, such as between pollinators and the flowers they pollinate.
- What is the function of the pollen tube during pollination?The pollen tube grows through the style to connect to the ovule and transmit male gametes or sperm.
- What is vegetative reproduction and what does it result in?Vegetative reproduction is a form of asexual reproduction in plants that results in genetically identical offspring or clones.
- What are rhizomes and stolons, and how do they differ?Rhizomes are underground stems that produce new individuals, while stolons are above-ground stems that also produce new individuals.
- What is apomixis in plants?Apomixis is the formation of seeds without fertilization, resulting in clone offspring.
- What is fragmentation in plant reproduction?Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction where plant fragments develop into mature organisms.
- What is vegetative propagation?Vegetative propagation is the human-assisted process of growing new plants from cuttings or clippings.
- What is the function of sepals in flowers?Sepals protect the flower buds and are generally green.
- What is the calyx in a flower?The calyx is the entire group of sepals and the cup-like structure they connect to.
- What is the corolla in a flower?The corolla is the entire group of petals in a flower.
- What are the male and female reproductive structures in flowers called?The male reproductive structures are called stamen, and the female reproductive structures are called carpals.
- What is the function of the anther in flowers?The anther contains the microsporangium, which produces microspores.
- What is the role of the stigma in flower reproduction?The stigma is the tip of the carpal where pollen lands and is received during reproduction.
- What is the function of the ovary in flowers?The ovary contains ovules, which receive sperm and develop into seeds after fertilization.
- how do some plants ensure cross-pollination? select all that apply.Plants ensure cross-pollination through mechanisms such as self-incompatibility, temporal separation (where male and female gametophytes mature at different times), and spatial avoidance (positioning male and female floral organs to prevent self-pollination).
- which part of the stamen looks like a stalk?The part of the stamen that looks like a stalk is the filament.